Reaction Report
Overview
Reaction Reports contain details about the individual reactions
that comprise signaling pathways. "Reaction" is a term used in BKL
to describe all kinds of interactions between signaling entities
(molecules or genes) in signaling
or regulatory events. The characteristics of each interaction, in
other words the effect of the interaction, are defined by an
effect term that appears on the Reaction
Report. Reactions as processes are not physical entities like
molecules, yet they are the central point in a signal transduction
database. By representing reactions between molecules as
separate Reaction Reports, it becomes possible to store their
properties and annotate them. Since many reactions in signal
transduction are catalyzed, and most catalyzed reactions are
quasi-unidirectional, all reactions stored in the database are by
default unidirectional. Equilibrium reactions, however, are
identified as "reversible" on the Reaction Report.
Four basic types of reactions are descibed: molecular evidence,
pathway step, decomposition, and semantic. These reaction types are
summarized in the table below.
Reaction Types
|
|
Semantic |
Pathway Step |
Decomposition |
Molecular Evidence |
|
Purpose |
Provides broad overview
of pathways or networks and shows the connectivity in a network.
The format often used in pathway graphics in reviews. |
Constitutes pathways that
depict the biochemical details of signal transduction cascades or
metabolic paths. |
Explains the mechanism
and identifies the acting molecules of reactions that occur in
complexes. Always linked to a pathway step reaction. |
Reflects the results of
experiments published in primary literature. Provides detail about
materials and methods used and indicates reliability of the
experimental approach. |
|
Mechanistic Notation* |
Not used |
Direct; metabolic |
Direct |
Direct |
|
Semantic Notation* |
Direct; indirect |
Indirect
(to bridge a gap in knowledge) |
Not present |
Indirect (if mechanism is
unknown) |
|
Molecule Hierarchy Level |
Orthofamily/ orthogroup/
orthobasic |
Orthofamily/ orthogroup/
orthobasic/ group (XOR)/ orthocomplex |
Orthofamily/ orthogroup/
orthobasic/ group (XOR)/ orthocomplex |
Family/ isogroup/ basic/
complex |
| States/
Modified Forms |
Implies states "active"
and "inactive" for the molecules. |
Used |
Used |
Used |
|
Molecule Roles |
Signal donor, signal
acceptor |
Reactant, enzyme,
inhibitor/ modifier, product |
Reactant, enzyme,
inhibitor/ modifier, product |
Reactant, enzyme,
inhibitor/ modifier, product |
*An illustration of semantic and mechanistic notations is shown
in Figure 1. Detailed
information about semantic and mechanistic reactions can be found
here.
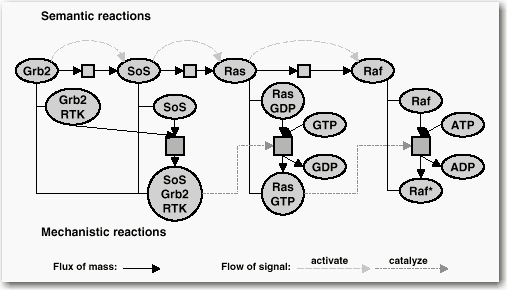
Figure 1.
Semantic and Mechanistic Reactions Semantic reactions
(small, light squares) go from SoS to Ras and from Ras to Raf,
implying that each of the molecules has two states, one "inactive"
state for receiving signals and an "active" state for transducing
signals. Mechanistic reactions (slightly darker, bigger squares)
are pathway steps and assign states explicitly to the
molecules.
Please note: Molecular evidence, pathway
step, and semantic reactions can be specified as direct or
indirect.
Please note: Metabolic reactions are curated
at the pathway step level only. They are assigned pathway step
metabolic.
Please note: Additional details about the
data model can be found in the following reference:
Choi C, Crass T, Kel A, Kel-Margoulis O, Krull M, Pistor S, Potapov
A, Voss N, Wingender E. (2004) Consistent re-modeling of
signaling pathways and its implementation in the TRANSPATH
database, Genome Inf Ser 15:244-254. [Abstract]
Each Reaction Report is similarly organized and comprises
different blocks for properties curated and references cited in the
Report. When additional details are provided, the property blocks
contain links to detailed Property
Reports. Other BKL Reports mentioned in the Reaction Report are
hyperlinked to the corresponding Reports. For example, individual
components of the reaction are listed on the Reaction Report, with
links to their corresponding Locus, Family, Complex, or Small Molecule Reports.
Reaction Reports may be accessed through the BKL Tools or through hyperlinks
on BKL reports.
Anatomy of a Reaction Report
The general structure of a Reaction Report is described below. A
reaction report will show several reactions, if the selected
reaction is part of the reaction
hierarchy. In addition to the selected and highlighted
reaction, its parents and children in the hierarchy will be
displayed. An overview is given in the navigator, while detailed
information about the reactions is shown below in the data
sections.
- Access help by clicking the help menu
 and clicking the Drug report help link.
and clicking the Drug report help link.
- Navigate to the desired section of the report by opening the
table of contents

Points of navigation within the report are indicated by the
following visual cues.
- Links to additional reports within the BKL are presented as
regular text links.
- Links to external resources are indicated by a blue bubble,
such as the PubMedID link shown here:
 .
.
- Links to display additional text within the page are indicated
by a yellow bubble, such as the show abstract link shown
here:
 .
.
- Links providing an option to send data to another tool within
the BKL are indicated by a gray bubble, such as the Pathfinder link
shown here:
 .
.
|
Semantic Reaction Information |
Describes the characteristics of the semantic-level reactions
associated with the reaction. |

|
|
RX#### |
Identifies a semantic-level reaction that is associated with the
reaction of the page, with hyperlinks to the corresponding Locus, Small Molecule, Family, or Complex Reports and the cited PubMed
reference. Click here for
detailed information about semantic-level reactions. If a curator
has added comments regarding particular functions or mechanisms
that provide additional detail about the reaction, a [Comments]
link appears, hyperlinked to a list of comments, or Annotations,
for the reaction. For a list of topics covered in Comments, click
here.
Note: Each semantic reaction associated with the Reaction Report
is displayed in an individual block on the Report. |
|
Effect |
|
Describes the effect(s) of the semantic reaction and identifies the
reaction as direct or indirect. Click here for a list of Effect terms. |
|
|
|
|
Pathway Step Reaction Information |
Describes the characteristics of the pathway step-level reactions
associated with the reaction. |
|
|
RX#### |
Identifies a pathway step-level reaction that is associated with
the reaction of the page, with hyperlinks to the corresponding
Locus, Small Molecule, Family, or Complex Reports and the cited PubMed
reference. Click here for
detailed information about pathway step-level reactions. If a
curator has added comments regarding particular functions or
mechanisms that provide additional detail about the reaction, a
[Comments] link appears, hyperlinked to a list of comments, or
Annotations, for the reaction. For a list of topics covered in
Comments, click here.
Note: Each pathway step reaction associated with the Reaction
Report is displayed in an individual block on the Report. |
|
Effect |
|
Describes the effect(s) of the pathway step reaction and identifies
the reaction as direct or indirect. Click here for a list of Effect terms. |
|
Pathways:Chains |
|
Lists pathways or chains the pathway step-level reaction is
associated with, with hyperlinks to the corresponding Pathway/Chain Reports. |
|
|
|
|
Molecular Evidence Reaction Information |
Describes the characteristics of the molecular evidence-level
reactions associated with the reaction. |
|
|
RX#### |
Identifies a molecular evidence-level reaction that is associated
with the reaction of the page, with hyperlinks to the corresponding
Locus, Small Molecule, Family, or Complex Reports and the cited PubMed
reference. Click here for
detailed information about molecular evidence-level reactions. If a
curator has added comments regarding particular functions or
mechanisms that provide additional detail about the reaction, a
[Comments] link appears, hyperlinked to a list of comments, or
Annotations, for the reaction. For a list of topics covered in
Comments, click here.
Note: Each unique molecular evidence reaction associated with
the Reaction Report is displayed in an individual block on the
Report. |
|
Effect |
|
Describes the effect(s) of the molecular evidence reaction and
identifies the reaction as direct or indirect. Click here for a list of Effect terms. |
|
Quality |
|
Indicates the reliability of the experiment performed to identify
the reaction, according to the TRANSPATH quality matrix. Click
here for additional details about how
combinations of materials and methods are associated with quality
scores. |
|
Experimental Source |
Indicates the source (cell line) for the material used in the
experiment that identified the molecular evidence reaction. Details
about the experimental source are accessible by clicking on
[details], which opens a
Property Report.
Note that in cases where multiple experiments have identified
the exact same reaction, the blocks that contains the Experimental
Source, Material, Method, and PMID eppear for each representative
experiment. |
|
Material |
|
Provides additional detail about the material used in the
experiment that identified the molecular evidence reaction. Click
here for additional details about
experimental materials. |
|
Method |
|
Indicates the method used to identify the reaction. Click here for additional details about experimental
methods. |
|
PMID |
|
Lists the PubMed identifier for the reference cited for the
molecular evidence reaction, hyperlinked to the PubMed
abstract. |
|
|
|
|
Decomposition Reaction Information |
Describes the characteristics of the decomposition reactions
associated with the pathway step reaction. |
|
|
RX#### |
Identifies a decomposition reaction that is associated with the
pathway step reaction of the page, with hyperlinks to the
corresponding Locus,
Small Molecule, Family, or Complex Reports and the cited PubMed
reference. Click here for
detailed information about decomposition and pathway step
reactions. If a curator has added comments regarding particular
functions or mechanisms that provide additional detail about the
reaction, a [Comments] link appears, hyperlinked to a list of
comments, or Annotations, for the reaction. For a list of topics
covered in Comments, click here.
Note: Each decomposition reaction associated with the Reaction
Report is displayed in an individual block on the Report. |
|
Effect |
|
Describes the effect(s) of the decomposition reaction and
identifies the reaction as direct or indirect. Click here for a list of Effect terms. |
|
|
|
|
References |
Displays list of references cited in the Reaction Report. |
|
|
This block gives the full citations, with titles, that correspond
to the PubMed identifiers displayed. When a PubMed identifier is
not available, the Medline identifier is displayed. When neither a
PubMed nor Medline identifier is available, a BIOBASE-specific
number is assigned preceded by a "P". Nearly all of the reference
numbers are hyperlinked to the Entrez database where the abstracts
may be read. All references cited in the annotations and properties
section are listed, and other references known to contain
information about the protein may also be listed. The first five
references are shown, click [ more ...] to view all references.
View abstracts via webservice, by additionally clicking the [+]
which appears. |
|
|

 and clicking the Drug report help link.
and clicking the Drug report help link.
 .
. .
. .
.