What's New
BKL 2024.2 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
JASPAR 2024 matrix library integration
New position frequency matrices from the JASPAR 2024 release either added as matrix entries (446 cases) or hyperlinked to existing counterparts in the TRANSFAC matrix library.
New enhancer data
2,045 new human and mouse enhancers have been integrated together with 2,693 high confidence enhancer - promoter interactions (EPI).
Enhanced human SNP content
The 2023 dbSNP release 156 data for human has been integrated and increases the number of SNPs mapped to promoter, enhancer, and silencer sequences by more than 13,800,000 new single nucleotide variatons compared to the previously used version 155.
Ensembl version update
Genomic information for genes, promoters, and ChIP fragments for the species human, mouse, rat, pig, macaque, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis is now based on Ensembl release 112.
Rat genome assembly update
TRANSFAC now uses rat genome assembly mRatBN7.2.
Additional interactions between human transcription factors
1,299 new human transcription factor interactions have been included from recent publications.
Biomarker and drug data update
The number of disease annotations increased to 414,870 and the number of unique
gene/biomarker - disease assignments to 137,060.
Newly FDA-approved drugs (Apr 2024 - Aug 2024) , their indication, and their protein target
information were added.
Increase in number of reactions
18,474 new binding reactions from recent publications between proteins in human have been added, e.g. from the chromosome 21 interactome.
BKL 2024.1 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Reactome integration
1,365 human pathways consisting of 12,786 reactions have been integrated and converted to the TRANSPATH data model. Subsequent reactions can be viewed in dedicated pathway reports and the Pathfinder tool visualizes whole pathways with options for e.g. editing and network expansion.
Increase in number of reactions
6,289 new binding reactions from recent publications between proteins in human and mouse have been added, e.g. from the human kinase interactome.
Update of links to Wikipathways
Links from genes/proteins to the pathway database Wikipathways (20240310) have been updated.
Biomarker and drug data update
The number of disease annotations increased to 408,644 and the number of unique gene/biomarker - disease assignments to 135,700.
Newly FDA-approved drugs (Sep 2023 - Mar 2024) , their indication, and their protein target information were added.
New TRANSFAC analysis tool
In its new 3.0 release, the MATCH Suite toolbox of TRANSFAC 2.0 was updated with the functionality of model organisms gene regulation analysis. Now, gene sets coming from Human, Mouse, or Rat can be analyzed in a new functional categorization-based analysis. You can specify certain transcription factors for narrowing down the site search to them, or you can select the functional categories of your interest and perform search only for transcription factors belonging to those GO terms. As usual, comprehensive report will be automatically generated with detailed description of the performed analysis steps, and interactive results visualization mode will allow you to fine-tune the obtained results by applying additional filters.
BKL 2023.2 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Integration of new human ChIP-Seq experiments from ENCODE
91 new human transcription factor binding site ChIP-Seq experiments released by the ENCODE phase 4
project have been integrated. The data sets comprise 1,029,262 fragments bound by 85 distinct
transcription factors, of which 33 factors were not yet covered by ChIP-Seq data in TRANSFAC.
For 58 of the sets, an existing positional weight matrix for the respective transcription factor
was used together with the MATCH tool to predict altogether 615,813 best binding sites inside the fragments.
Predicted best binding sites as well as complete fragments are available in FASTA and BED format via the
ChIP Experiment Reports, as are lists of genes in a distance range to the fragments as specified by the user.
New matrices derived from ENCODE ChIP-Seq data
24 new positional weight matrices for yet uncovered human transcription factors have been generated from new ENCODE phase 4 ChIP-Seq data and integrated into the TRANSFAC matrix library.
Biomarker and drug data update
The number of disease annotations increased to 397,877 and the number of unique gene/biomarker - disease assignments to 133,533.
378 drugs and 2,392 protein targets were added.
Increase in number of reactions
34,829 new binding reactions from recent publications between proteins in human, mouse, and rat have been added. In addition, 7,531 phosphorylation reactions by human receptor tyrosine kinases (RTK) were included.
Update of links to Wikipathways and Reactome
Links from genes/proteins to the pathway databases Wikipathways (20230810) and Reactome (v85) have been updated.
BKL 2023.1 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Biomarker and drug data update
The number of disease annotations increased to 390,340 and the number of unique
gene/biomarker - disease assignments to 132,237.
22 recently FDA approved drugs and their protein targets were added.
More recursive search options
"Search within" option for gene expression regulator data available to be combined with 11 other search categories.
Better performance
Server hardware update allows for faster report loading times.
Increase in number of reactions
46,322 new binding reactions from recent publications between proteins in human have been added, among them e.g. from the protein kinase network.
Update of links to Wikipathways and Reactome
Links from genes/proteins to the pathway databases Wikipathways (20230310) and Reactome (v83) have been updated.
JASPAR 2022 matrix library integration
New position frequency matrices from the JASPAR 2022 release either added as matrix entries (375 cases) or hyperlinked to existing counterparts in the TRANSFAC matrix library.
Additional interactions between human transcription factors
13,100 new human transcription factor interactions have been included from BIOGRID.
Integration of new human ChIP-Seq experiments from ENCODE
162 new human transcription factor binding site ChIP-Seq experiments released by the ENCODE phase 4
project have been integrated. The data sets comprise 1,700,273 fragments bound by 143 distinct
transcription factors, of which 39 factors were not yet covered by ChIP-Seq data in TRANSFAC.
For 134 of the sets, an existing positional weight matrix for the respective transcription factor
was used together with the MATCH tool to predict altogether 1,316,751 best binding sites inside the fragments.
Predicted best binding sites as well as complete fragments are available in FASTA and BED format
via the ChIP Experiment Reports, as are lists of genes in a distance range to the fragments as specified by the user.
New matrices derived from ENCODE ChIP-Seq data
12 new positional weight matrices for yet uncovered human transcription factors have been generated from new ENCODE phase 4 ChIP-Seq data and integrated into the TRANSFAC matrix library..
BKL 2022.2 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
More predicted enhancer - promoter interactions to identify target genes
57,038 additional enhancer - target gene relations have been imported from the FOCS web site.
Additional interactions between human transcription factors
7,949 human transcription factor interactions have been included from a recent publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35140242/).
Integration of new human ChIP-Seq experiments from ENCODE
70 new human transcription factor binding site ChIP-Seq experiments released by the ENCODE phase 4 project and further publications have been integrated. The data sets comprise 603,016 fragments bound by 66 distinct transcription factors, of which 19 factors were not yet covered by ChIP-Seq data in TRANSFAC. For 54 of the sets, an existing positional weight matrix for the respective transcription factor was used together with the MATCH tool to predict altogether 436,596 best binding sites inside the fragments. Predicted best binding sites as well as complete fragments are available in FASTA and BED format via the ChIP Experiment Reports, as are lists of genes in a distance range to the fragments as specified by the user.
Biomarker and drug target data update
The number of disease annotatons increased to 378,522 and the number of unique gene/biomarker - disease assignments to 129,784. Targets for FDA - approved drugs have been added by manual curaton and the number of drug - target protein associatons is now 53,034.
Increase in number of reactons
47,303 new binding reactons from recent publicatons between proteins in human have been added, among them e.g. from the OpenCell and the COVID19 interactome.
Update of links to Wikipathways and Reactome
Links from genes/proteins to the pathway databases Wikipathways (20220810) and Reactome (v81) have been updated.
BKL 2022.1 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
MATCH Suite: Single gene analysis
In its release 2.0 MATCH Suite now supports gene regulation analysis for
single genes in addition to the previously introduced gene set studies. Specify
the gene of your interest using its gene symbol, Entrez or Ensembl ID, and find
the transcription factors responsible for regulation of your gene via its promoter
and enhancers/silencers.
You can optionally select the tissue of your interest, the promoter type and region
to be used for the analysis, or the GO terms to narrow down the identified
transcription factors to the ones belonging to the chosen biological processes.
The analysis results will provide you with lists transcription factors (TFs)
and respective binding sites that were predicted to regulate the specified gene
in the selected conditions. Interactive visualization in genome browser will
allow to observe the predicted and experimentally proven TF binding sites in
the promoter and enhancers/silencers of your gene in the specified tissue
(if any was selected). Analysis report will provide you with comprehensive
information on the performed analysis and the obtained results.
Extended options to use search results as input for further queries
Transcription factors that bind to regulatory regions of specific genes in
ChIP-Seq experiments, can now be queried directly from a gene/protein search
result. This extends the possibility to identify regulatory factors for a
gene beyond the ones found through DNA binding sites from low-throughput experiments.
Other added options include the possibilities to query for drugs approved
or under research for a certain condition from a search result of diseases and vice versa.
Integration of new human ChIP-Seq experiments from ENCODE
17 new human transcription factor binding site ChIP-Seq experiments released
by the ENCODE phase 4
project have been integrated. The data sets comprise 38,319 fragments bound by
17 distinct transcription factors, of which 10 factors were not yet covered by
ChIP-Seq data in TRANSFAC.
For 14 of the sets, an existing positional weight matrix for the respective
transcription factor was used together with the MATCH tool to predict altogether
28,204 best binding sites inside the fragments.
Predicted best binding sites as well as complete fragments are available in
FASTA and BED format via the ChIP Experiment Reports, as are lists of genes
in a distance range to the fragments as specified by the user.
Quantitative tissue expression diagram in human locus reports
Normalized transcript expression levels from Human Protein Atlas (v20) are displayed in a histogram across 61 different cell types/tissues. There are several sorting and grouping options, e.g. cell/tissue by organ. In addition, a value for the relative tissue specificity as indicator for expression ubiquity of the respective human gene is given.
Biomarker and drug target data update
The number of disease annotations increased to 369,215 and the number of unique gene/biomarker - disease assignments to 126,804. Targets for FDA - approved drugs have been added by manual curation and the number of drug - target protein associations is now 51,827.
Increase in number of reactions
57,268 new binding reactions from recent publications between proteins in human and mouse have been added, among them e.g. from the brain and kidney interactome.
Update of links to Wikipathways and Reactome
Links from genes/proteins to the pathway databases Wikipathways (20220110) and Reactome (v78) have been updated.
BKL 2021.3 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
New silencer data
31,933 human and mouse silencer sequences have been imported from the SilencerDB database and lifted over to the GRCh38 and GRCm39 genome assemblies. Like enhancer reports, silencer reports display genes with which promoters the silencer interacts, tissues and cell types/lines the silencer is active in, and genomic regions such as histone modification sequences, DNase I hypersensitivity sites, and transcription factor binding sites that overlap with the silencer.
Integration of new human ChIP-Seq experiments from ENCODE
83 new human transcription factor binding site ChIP-Seq experiments
released by the ENCODE phase 4
project have been integrated. The data sets comprise 588,473 fragments
bound by 79 distinct transcription factors, of which 51 factors were not
yet covered by ChIP-Seq data in TRANSFAC.
For 47 of the sets, an existing positional weight matrix for the
respective transcription factor was used together with the MATCH tool
to predict altogether 388,362 best binding sites inside the fragments.
Predicted best binding sites as well as complete fragments are available
in FASTA and BED format via the ChIP Experiment Reports, as are lists of
genes in a distance range to the fragments as specified by the user.
Enhanced human SNP content
The 2021 dbSNP release 155 data for human has been integrated and increases the number of SNPs mapped to promoter, enhancer, and silencer sequences by more than 72,000,000 new single nucleotide variatons compared to the previously used version 154.
Ensembl version update
Genomic information for genes, promoters, and ChIP fragments for the species human, mouse, rat, pig, macaque, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis is now based on Ensembl release 104.
Mouse genome assembly update
TRANSFAC now uses the latest mouse genome assembly GRCm39 (mm39).
Biomarker and drug target data update
The number of disease annotations increased to 363,661 and the number of unique gene/biomarker - disease assignments to 125,437. Targets for FDA - approved drugs have been added by manual curation and the number of drug - target protein associations is now 48,465.
Increase in number of reactions
24,118 new binding reactions from recent publications between proteins in human have been added, among them e.g. from the midbody and cilia-specific interactome. For 5,164 of these reactions, information on their intracellular location has been annotated.
Update of links to Wikipathways
Links from genes/proteins to the pathway database Wikipathways (20211010) have been updated.
BKL 2021.2 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
TRANSFAC 2.0: Introducing the MATCH Suite
This software package has been optimized to identify transcription factors and their combinations that regulate the genes of your interest. MATCH Suite accepts human gene lists as input (either your own gene lists uploaded to the system or genes selected in the search results from the TRANSFAC, TRANSPATH or HumanPSD databases) and initializes a fully automatized sophisticated workflow, which produces the static analysis report and interactive tables of found factors and their binding sites. On-the-fly filtering by different criteria as well as the interactive genome browser visualization of sites identified in the promoters of the input genes is provided by the system in a user-friendly interface. MATCH Suite considers the biological context of your data, including functional categories or tissue specificities of your input genes, and provides you with the information on transcription factors and their combinatory modules that were identified to be regulating your input gene set. You can explore the User guide of the MATCH Suite here.
New enhancer reports
199,183 human enhancer sequences have been imported from FANTOM5 and the HACER database and lifted over to the GRCh38 genome assembly. The enhancer reports display genes with which promoters the enhancer interacts, tissues and cell types/lines the enhancer is active in, and genomic regions such as histone modification sequences, DNase I hypersensitivity sites, and transcription factor binding sites that overlap with the enhancer.
Additional transcription factor interactions
3,888 new interactions between human transcription factor proteins from, among others, the recently published BIOPLEX 3 data set and the human reference interactome (HuRI) have been included.
Integration of new human ChIP-Seq experiments from ENCODE
15 new human transcription factor binding site ChIP-Seq experiments released
by the ENCODE phase 4 project
have been integrated. The data sets comprise 197,893 fragments bound by 13
distinct transcription factors, of which 5 factors were not yet covered by
ChIP-Seq data in TRANSFAC.
For 13 of the sets, an existing positional weight matrix for the respective
transcription factor was used together with the MATCH tool to predict
altogether 174,539 best binding sites inside the fragments.
Predicted best binding sites as well as complete fragments are available in
FASTA and BED format via the ChIP Experiment Reports, as are lists of genes
in a distance range to the fragments as specified by the user.
Ensembl version update
Genomic information for genes, promoters, and ChIP fragments for the species human, mouse, rat, pig, macaque, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis is now based on Ensembl release 102.
Biomarker and drug data update
The number of disease annotations increased to 358,353 and the number of unique gene/biomarker - disease assignments to 123,948. New FDA - approved drugs have been added and the number of drug - target protein associations is now 47,504.
BIOPLEX 1 and 3 interactome data imported
Integration of BIOPLEX human interaction data from release 1 and 3 resulted in 131,566 new and 60,151 reactions updated with additional experimental evidence.
Human Reference Protein Interactome (HuRI) integrated
45,468 new reactions were imported from the HuRI mapping project. In addition, 6,371 existing reactions were updated with experimental evidence from HuRI.
Additional increase in number of reactions
29,662 new binding reactions between proteins in human have been added, among them e.g. from interactome in mitochondria and the bromodomain protein interactome.
Update of links to pathway databases
Links from genes/proteins to the pathway databases Reactome (version 77) and Wikipathways (20210610) have been updated.
BKL 2021.1 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
New locus report structure
The content of the reports containing gene and protein information associated with a specific genomic locus has been given a more accessible and intuitive structure.
New pathway visualization program
The new software replaces the old Flash-dependent Pathfinder. It provides pathway visualization detailing the location of molecules in the main intracellular compartments. Designed as a specialized Pathfinder perspective in the broader geneXplain bioinformatics platform, it supports product integration and provides the possibility to extend data analysis with a vast set of systems biology applications and workflows.
More clinical trial and biomarker data
New data from clinicaltrials.gov, the AACT and manual disease biomarker curation by experts have increased the number of CT-Disease-Drug assignments to 706,055 and the number of disease annotations to 348,831.
Increase in number of reactions
3,881 new binding reactions between proteins in human have been added, among them e.g. from the MAP4K interactome and the Ras interactome.
Update of links to pathway databases
Links from genes/proteins to the pathway databases Reactome (version 75) and Wikipathways (20201110) have been updated.
Integration of new human ChIP-Seq experiments from ENCODE
415 new human transcription factor binding site ChIP-Seq
experiments released by the
ENCODE phase 4 project between June 2020 and September 2020
have been integrated. The data sets comprise 4,768,755 fragments
bound by 391 distinct transcription factors, of which 214 factors
were not yet covered by ChIP-Seq data in TRANSFAC.
For 336 of the sets, an existing positional weight matrix for the
respective transcription factor was used together with the MATCH
tool to predict altogether 3,652,932 best binding sites inside the
fragments.
Predicted best binding sites as well as complete fragments are
available in FASTA and BED format via the ChIP Experiment Reports,
as are lists of genes in a distance range to the fragments as
specified by the user.
New matrices derived from ENCODE ChIP-Seq data
128 new positional weight matrices have been generated from new ENCODE phase 4 ChIP-Seq data and integrated into the TRANSFAC matrix library.
JASPAR 2020 matrix library integration
New position frequency matrices from the JASPAR 2020 release either added as matrix entries (200 cases) or hyperlinked to existing counterparts in the TRANSFAC matrix library.
Ensembl version update
Genomic information for genes, promoters, and ChIP fragments for the species human, mouse, rat, pig, macaque, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis is now based on Ensembl release 101.
BKL 2020.3 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Quick access box on start page
Browse all human gene, disease, and drug entries in HumanPSD and access the detailed reports directly.
Keyword Search
UniProtKB accessions, EntrezGene IDs, and BKL primary and secondary accessions can now be used as input in a keyword search.
Disease entry for COVID-19
A dedicated entry for COVID-19 based on data from the MeSH 2021 preview release was included. It contains more than 1,900 clinical trials related to the disease provided by the AACT database and clinicaltrials.gov.
More Clinical Trial and Biomarker data
New data from clinicaltrials.gov and manual
disease biomarker curation by experts have increased the number of
CT-Disease-Drug assignments to 695,136 and the number of disease
annotations to 344,832.
Improved processing of clinical trials data using the AACT database has contributed to these elevated numbers.
Increase in number of reactions
15,202 new binding reactions between proteins in human have been added, among them e.g. from the IFN-beta stimulated and unstimulated interactome or the beta-actin interactome.
Interactions between SARS-CoV-2 and human proteins
For 26 SARS-CoV-2 proteins, 330 interactions with protein targets in human cells were imported (Gordon, D. E. et al., Nature 583, 459-468 (2020), Pubmed 32353859).
Update of links to pathway databases
Links from genes/proteins to the pathway databases Reactome (version 73) and Wikipathways (20200710) have been updated. Wikipathways links now also include zebra fish (Danio rerio) and SARS-CoV-2 related pathways.
Extended range of species for Match / FMatch upload
Genomic intervals in BED format from the species Drosophila melanogaster, rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta), and pig (Sus scrofa) can now be uploaded as input for the analysis tools Match, Fmatch, and Composite model search, allowing to search for (overrepresented) transcription factor binding sites or binding site pairs in the promoter sequences of these species.
Additional files in the TRANSFAC and associated TRANSPro download packages
For TRANSFAC files in JSON format, there is a short guide and
example scripts how to import them into a PostgreSQL database and
have the advantage to join and query data from separate files.
The TRANSPro package now contains promoter data in Gene
Transfer Format (GTF) for the species human, mouse, rat, pig,
rhesus macaque, Drosophila melanogaster, and Arabidopsis
thaliana.
Enhanced human SNP content
The 2020 dbSNP release 154 data for human has been integrated and increases the number of SNPs mapped to human promoter sequences by more than 10,000,000 new single nucleotide variations compared to the previously used version 151.
Ensembl version update
Genomic information for genes, promoters, and ChIP fragments for the species human, mouse, rat, pig, macaque, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis is now based on Ensembl release 100.
BKL 2020.2 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Disease-disease associations
Disease reports have been enriched with inferred disease-disease relationships on the basis of shared causal biomarker genes. Disease vicinity networks visualize clusters of diseases with apparent biomedical relevance. Heatmaps illustrate connections between causal biomarker genes and clustered diseases. More details...
More Clinical Trial and Biomarker data
New data from clinicaltrials.gov and manual
disease biomarker curation by experts have increased the number of
CT-Disease-Drug assignments to 564,793 and the number of disease
annotations to 338,651.
More than 350 additional FDA-approved drugs and improved processing
of clinical trials data using the AACT database have
contributed to these elevated numbers.
Increase in number of reactions
5,112 new binding reactions between proteins in human, mouse, and rat have been added, among them e.g. from the AMPK interactome and ALS-associated proteins.
Update of links to pathway databases
Links from genes/proteins to the pathway databases Reactome (version 71) and Wikipathways (20200210) have been updated. Wikipathways links now also include Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Drosophila melanogaster.
Pathway reports with more information
Participating proteins in a pathway are now listed with a short summary of their functional properties to allow quicker assessment of their role in the network.
Integration of new p53 ChIP-Seq experiments
A comparative study of human binding site ChIP-Seq data for the
transcription factor p53 in 12 different cell lines has been
integrated (Hafner, A. et al., BMC Mol. Cell Biol. 21 (2020),
Pubmed 32070277).
Likewise, a study of p53 ChIP-Seq binding sites in the developing
embryonic mouse kidney has been added (Li, Y. et al., Physiol.
Genomics 45 (2013), Pubmed 24003036).
Protein-protein interactions of transcription factors
350 new binding reactions of the transcription factors BCL11B and c-Krox (Zbtb7b) to other proteins have been included.
Ensembl version update
Genomic information for genes, promoters, and ChIP fragments for the species human, mouse, rat, pig, macaque, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis is now based on Ensembl release 99.
BKL 2020.1 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Human microRNA - mRNA interactome
42,700 new microRNA interacting mRNA sites associated with 10,864 distinct human genes were included. They had been collected and analyzed in "Plotnikova, O. et al, Comprehensive Analysis of Human microRNA-mRNA Interactome, Front. Genet. 2019 10:933, Pubmed PMID: 31649721". 440 distinct human mircoRNAs were identified to interact with the imported set of mRNA sites.
Integration of new human ChIP-Seq experiments from ENCODE
39 new human transcription factor binding site ChIP-Seq
experiments released by the
ENCODE phase 4 project in 2019 have been integrated. The data
sets comprise 1,170,688 fragments bound by CTCF (CCCTC-binding
factor).
For all of the sets, an existing positional weight matrix for CTCF
was used together with the MATCH tool to predict altogether
1,084,822 best binding sites inside the fragments.
Ensembl version update
Genomic information for genes, promoters, and ChIP fragments for the species human, mouse, rat, pig, macaque, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis is now based on Ensembl release 98. This includes a new genome assembly for macaque (Mmul_10, Feb 2019).
External disease identifiers added
External identifiers and hyperlinks to disease classifications and ontologies such as ICD10, Snomed CT or NCI thesaurus have been included based on data from the Mondo Disease Ontology and the Disease Ontology (DO). In total, 26,615 external references have been added to 2,817 distinct disease reports.
More Clinical Trial and Biomarker data
New data from clinicaltrials.gov and manual disease biomarker curation by experts have increased the number of CT-Disease-Drug assignments to 424,169 and the number of disease annotations to 333,184.
Increase in number of reactions
1,450 new binding reactions between proteins in human and in mouse have been added, among them e.g. reactions of the human KRAB zinc finger protein or the mouse GAP/GEF protein interactome.
BKL 2019.3 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Locus report links to Reactome pathways
Many locus reports now contain a table with Reactome pathways the gene/protein is involved in. More than 100,000 hyperlinks to pathway reports in Reactome (version 69) as well as to the Reactome pathway browser have been added.
More Clinical Trial and Biomarker data
New data from clinicaltrials.gov and manual disease biomarker curation by experts have increased the number of CT-Disease-Drug assignments to 412,475 and the number of disease annotations to 329,469.
Increase in number of reactions
7,506 new binding reactions between proteins in human, mouse, rat or fruit fly have been added, among them e.g. reactions from the human ER-alpha and O-GlcNAc transferase interactome. New phosphorylation targets have been included by integrating 526 reactions catalyzed by the human serine/threonine kinase PRKD3.
Increase in Drosophila melanogaster transcription factor interactions
More than 2,500 protein-protein interactions from the transcription factor network in fruit flies have been added. They were published in "Shokri, L. et al, A Comprehensive Drosophila melanogaster Transcription Factor Interactome, Cell Rep. 2019, 27(3):955-970, Pubmed PMID: 30995488" and in "Rhee, D. Y. et al., Transcription factor networks in Drosophila melanogaster, Cell Rep. 2014, 8(6):2031-2043, Pubmed PMID: 25242320".
miRNA target site import from miRTarBase
3,634 new experimentally verified miRNA target sites have been added from miRTarBase 7.0. The microRNAs and their mRNA sites are from a range of species, but predominantly from human and mouse. Also, 337 existing sites in TRANSFAC were updated with further experimental evidence from miRTarBase.
Matrix, Factor and Site flat files in JSON format
To simplify data integration and interchange, TRANSFAC download customers can obtain the three flat files in JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) format in addition to the traditional format. JSON is supported by a rich infrastructure of tools in all modern languages and has become the de facto standard for data interchange.
Extended binding transcription factors for gene search result
When you want to find out which transcription factors bind and regulate a set of genes based on experimentally verified data, this can be done by concatenating searches, i.e. run a second "binding factors for gene" search using the result of a gene search (by keyword or as gene list upload) as input. The result of this second query now includes the regulatory effect (activation or repression) the factor has on the gene, if this is known.
Ensembl version update
Genomic information for genes, promoters, and ChIP fragments for the species human, mouse, rat, pig, macaque, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis is now based on Ensembl release 96.
BKL 2019.2 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Matrices for methylated binding motifs
1,785 matrices for human transcription factors from Methyl-HT-SELEX and HT-SELEX experiments were added. They were published in "Yin, Y. et al, Impact of cytosine methylation on DNA binding specificities of human transcription factors, Science 2017 356(6337):eaaj2239, Pubmed PMID: 28473536". Based on the selection of representative methylated motifs, a specific matrix profile has been added to be used with MATCH.
Drosophila melanogaster promoters added
19,152 promoters for fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) have been included based on data from Ensembl version 95 and our established virtual transcription start site calculation. Experimentally verified transcription factor binding sites and 3.6 million SNPs from the dbSNP database have been mapped to the promoter sequences.
Annotation of transcription factor binding sites based on sequence conservation
Known transcription factor binding sites located in human, mouse, rat, or pig genomes were extracted from TRANSFAC® and highly conserved sites were retained. Given high conservation as a prerequisite, binding sites were annotated for the three other species in respective genomic location if not more than one mismatch was observed in the sequence alignment with the primary species. This resulted in 1,007 new binding site entries.
Integration of new human and fruit fly ChIP-Seq experiments from ENCODE, modENCODE and modERN
21 new human transcription factor binding site ChIP-Seq experiments released by the ENCODE phase 3 and 4 project between July 2018 and December 2018 have been integrated. The data sets comprise 424,961 fragments bound by 15 distinct transcription factors. For Drosophila melanogaster, 470 transcription factor binding site ChIP-Seq experiments released by the modENCODE and modERN were added. The data sets include 2,050,835 fragments bound by 411 distinct transcription factors, all of which were not yet covered by TRANSFAC ChIP-Seq data. For 183 of the sets, an existing positional weight matrix for the respective transcription factor was used together with the MATCH tool to predict altogether 953,185 best binding sites inside the fragments.
Ensembl version update
Genomic information for genes, promoters, and ChIP fragments for the species human, mouse, rat, pig, macaque, Drosophila, and Arabidopsis is now based on Ensembl release 95.
More Clinical Trial data
New data from clinicaltrials.gov and manual curation by experts have increased the number of Clinical Trial-Drug assignments to 204,740, leading to a total of 401,836 CT-Disease-Drug assignments.
GO cellular compartment annotation from the Human Protein Atlas
Intracellular location data of human proteins from the Human Protein Atlas has been integrated as 12,073 observations using Gene Ontology Cellular Compartment terms.
Increase in number of reactions
18,087 new binding reactions between proteins in human or mouse
have been added, among them e.g. reactions of membrane-bound human
GPCRs with other membraneous or cytoplasmic proteins.
5,071 existing reactions were updated with additional experimental
evidences from primary literature.
Improved pathway search results
Pathway search results now come with the number of distinct nodes (proteins and their post-translationally modified forms, genes, miRNAs, and complexes) involved in the respective pathway. This should help with assessing the size of networks in a result list.
BKL 2019.1 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Matrices for C2H2 zinc finger transcription factors
130 matrices derived from ChIP-Seq experiments involving TFs from the C2H2 zinc finger family have been included. They were published in "Schnitges, F. W. et al, Multiparameter functional diversity of human C2H2 zinc finger proteins, Genome Res. 2016 26:1742-1752, Pubmed PMID: 27852650 alongside with 1,292 interactions of C2H2 factors with nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins.
Pig promoters added
27,812 promoters for pig (Sus scrofa) have been included based on data from Ensembl version 94 and our established virtual transcription start site calculation. Experimentally verified transcription factor binding sites and 6 million SNPs from the dbSNP database have been mapped to the promoter sequences.
Interactions between Arabidopsis thaliana transcription factors
8,456 new and 31 updated interactions between Arabidopsis transcription factors have been added based on data published in "Trigg, S. A. et al, CrY2H-seq: a massively multiplexed assay for deep-coverage interactome mapping. Nat. Methods 2017, 14(8):819-825, PubMed PMID: 28650476.
Ensembl version update
Genomic information for genes, promoters, and ChIP fragments for the species human, mouse, rat, pig, macaque, and Arabidopsis is now based on Ensembl release 94.
Increase in number of reactions
19,231 new binding reactions between proteins in human or Arabidopsis thaliana have been added, among them e.g. reactions from the human aging-related interactome. 1,078 existing reactions were updated with additional experimental evidences from primary literature.
Links to Wikipathways
Genes/proteins from human, mouse, rat, Arabidopsis, and yeast are now linked to the respective signalling and metabolic pathways from Wikipathways. The pathways can be directly displayed on the gene/protein's locus report.
More Clinical Trial data
New data from clinicaltrials.gov and manual curation by experts have increased the number of Clinical Trial-Drug assignments to 203,347, leading to a total of 398,810 CT-Disease-Drug assignments.
Custom search for complexes
Dedicated search for complexes by different data types is now available as part of the SQL-like custom search system. The resulting list of complexes can also be used as input for queries for connected entities, such as reactions or transcription factor binding sites.
Functional analysis
Under-represented GO terms or pathways are now indicated more clearly in the result's summary chart.
BKL 2018.3 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Human Protein Atlas version 18 data integration
This release includes more than 1.9M protein and RNA expression observations in human tissues/organs, cell types and tumors imported from the Human Protein Atlas.
More Clinical Trial data
New data from clinicaltrials.gov, ChEMBL v24, and manual curation by experts have increased the number of Clinical Trial-Drug assignments to 199,098, leading to a total of 390,258 CT-Disease-Drug assignments.
Drug targets and metabolizing enzymes from ChEMBL
14,659 drug - protein target and enzyme - drug relationships have been imported from ChEMBL v24.
miRBase v22 update included for species covered by HumanPSD
Besides updates for existing entries, the new miRBase version integration provides 175 new precursor miRNA and 235 new mature miRNAs.
Significant increase in number of reactions
45,352 new binding reactions between proteins in human and mouse have been added, among them e.g. interactions from non-canonical NF-kappaB signalling or the interactome associated with autism disorders. 3,305 existing reactions were updated with additional experimental evidences from primary literature.
HOCOMOCO v11 core collection added to matrix library
311 human and 250 mouse matrices from HOCOMOCO's v11 core collection of transcription factor binding models have been imported.
Integration of new human ChIP-Seq experiments from ENCODE
38 new human transcription factor binding site ChIP-Seq
experiments released by the
ENCODE phase 3 project between February 2018 and May 2018 have
been integrated. The data sets comprise 690,754 fragments bound by
29 distinct transcription factors, of which 12 factors were not yet
covered by ChIP-Seq data.
For 14 of the sets, an existing positional weight matrix for the
respective transcription factor was used together with the MATCH
tool to predict altogether 436,024 best binding sites inside the
fragments.
Predicted best binding sites as well as complete fragments are
available in FASTA and BED format via the ChIP Experiment Reports,
as are lists of genes in a distance range to the fragments as
specified by the user.
Interactions between transcription factors
1,529 new and 114 updated human and mouse interactions between transcription factors have been added based on data published in "Ravasi T. et al, An atlas of combinatorial transcriptional regulation in mouse and man. Cell. 2010 Mar 5;140(5):744-52, PubMed PMID: 20211142".
Enhanced human SNP content
The new 2018 dbSNP Build 151 data for human has been integrated and increases the number of SNPs mapped to human promoter sequences from 73,423,232 in the last release to 142,487,394.
Ensembl version update
Genomic information for genes, promoters, and ChIP fragments for the species human, mouse, rat, macaque, and Arabidopsis is now based on Ensembl release 93.
BKL 2018.2 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Performance assessment of TRANSFAC PWMs and derived matrix recommendations
Out of the huge collection of PWMs in the TRANSFAC database, a
non-redundant library was compiled comprising the best-performing
DNA-binding motifs of altogether 2799 transcription factors.
The user can now choose among four new PWM profiles consisting of
recommended matrices for vertebrate, plant, fungal, and insect
factors to be used with MATCH (to predict transcription factor
binding sites, TFBSs, in DNA sequences) or FMATCH (to identify
enriched TFBSs in a set of DNA sequences).
Integration of new human ChIP-Seq experiments from ENCODE
164 new human transcription factor binding site ChIP-Seq
experiments released by the
ENCODE phase 3 project between October 2017 and January 2018
have been integrated. The data sets comprise 2,570,897 fragments
bound by 122 distinct transcription factors, of which 68 factors
were not yet covered by ChIP-Seq data. For 76 of the sets, an
existing positional weight matrix for the respective transcription
factor was used together with the MATCH tool to predict altogether
1,497,691 best binding sites inside the fragments.
Predicted best binding sites as well as complete fragments are
available in FASTA and BED format via the ChIP Experiment Reports,
as are lists of genes in a distance range to the fragments as
specified by the user.
Addition of public human ChIP-Seq experiments from other sources
1,757 human ChIP-Seq data sets published in GEO and ArrayExpress and re-analyzed by the ReMap 2018 project have been incorporated. The experiments involve 48,509,720 fragments bound by 342 distinct transcription factors, including 190 without previous ChIP-Seq data set in the database. The peaks were taken from the âall peaksâ catalog, allowing to preserve the cell specificity of the original experiments.
Ensembl version update
Genomic information for genes, promoters, and ChIP fragments for the species human, mouse, rat, macaque, and Arabidopsis is now based on Ensembl release 91.
Increased number of interventions in clinical trials mapped to drugs
New data from clinicaltrials.gov and manual curation by experts has increased the number of Clinical Trial-Drug assignments to 172,962.
Cancer biomarkers
A shift in curation to yet underrepresented neoplasms (such as mouth or esophageal cancer) in the database has increased the number of gene â disease assignments to 110,961.
Human phosphatases interactome
5,412 new or updated reactions detailing the interactome and substrates of human phosphatases from recent publications.
BioPlex integration
57,890 reactions have been added or updated with additional experimental evidence by incorporating the BioPlex 2.0 network of human protein interactions.
BKL 2018.1 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Increased transcription factor coverage for 38 mammalian species
Based on the recently published new version of TFClass, the Classification of Transcription Factors in Mammalia, more than 23,000 factor entries from 38 species such as sheep, dog, or macaque have been added and linked to their human orthologs via the transcription factor classification.
Integration of mouse and new human ChIP-Seq experiments from ENCODE
76 new human transcription factor binding site ChIP-Seq
experiments released by the
ENCODE phase 3 project between June 2017 and September 2017
have been integrated. To increase mouse data coverage, 140 TFBS
ChIP-Seq data sets, also from ENCODE, have been added. In total,
the experiments comprise 4,893,699 fragments bound by 94 distinct
transcription factors, of which 53 factors were not yet covered by
ChIP-Seq data.
For 128 of the sets, an existing positional weight matrix for the
respective transcription factor was used together with the MATCH
tool to predict altogether 3,215,450 best binding sites inside the
fragments. Predicted best binding sites as well as complete
fragments are available in FASTA and BED format via the ChIP
Experiment Reports, as are lists of genes in a distance range to
the fragments as specified by the user.
JASPAR 2018 matrix library integration
New position frequency matrices from the JASPAR 2018 release either added as matrix entries (57 cases) or hyperlinked to existing counterparts in the TRANSFAC matrix library.
Ensembl version update
Genomic information for genes, promoters, and ChIP fragments for the species human, mouse, rat, macaque, and Arabidopsis is now based on Ensembl release 90.
Improved biomarker retrieval from disease reports
Biomarkers can be retrieved by type of association with the disease or by indication for the utility of the biomarker, matching the categories of the biomarker association table in a disease report. The sets of biomarkers can be exported or used as input for the PathwayBuilder visualization tool or processed by other tools.
Increased number of conditions in clinical trials mapped to diseases
New data from clinicaltrials.gov and manual curation by experts has increased the number of Clinical Trial-Disease assignments to 664,258, leading to 362,881 CT-Disease-Drug assignments.
Cancer pathway list
The canonical signal transduction pathway overview page now contains a section for pathways involved in the development of various types of cancer.
BKL 2017.3 Release (TRANSFAC, HumanPSD and TRANSPATH)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Annotation of transcription factor binding sites based on sequence conservation
Known transcription factor binding sites located in human, mouse
or rat genomes were extracted from TRANSFAC® and highly
conserved sites were retained. Given high conservation as a
prerequisite, binding sites were annotated for the two other
species in respective genomic location if not more than one
mismatch was observed in the sequence alignment with the primary
species. This resulted in 1,565 new binding site entries.
High conservation was determined using PhastCons [1] probabilities
available from the UCSC genome server (https://genome.ucsc.edu/). A binding
site was assumed to be highly conserved if all DNA bases were
conserved with at least 99% probability according to PhastCons's
inference. Conserved human sites were found based on the 20-way
alignmnent of the human genome (http://hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/hg38/phastCons20way/)
to 19 mammalian (including 16 primate) genomes. Annotation of
conserved sites in mouse used the 60-way alignment of the mouse
genome to 59 vertebrate genomes ( http://hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/mm10/phastCons60way/),
and conservation of binding sites in the rat genome was determined
on the basis of the 20-way alignment of the rat genome to 19
vertebrate genomes ( http://hgdownload.soe.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/rn6/phastCons20way/).
The new binding site annotations were assigned to orthologous
transcription factors using the TFClass hierarchy [2]. In cases
where the already existing conserved binding site lacked the link
to the transcription factor from the same species due to an
heterologous experimental setup, that link was introduced with this
update.
- Pollard, K.S., Hubisz M.J., Rosenbloom K.R., Siepel A. Detection of nonneutral substitution rates on mammalian phylogenies. Genome Res. 20, 110-121 (2010).
- Wingender, E., Schoeps, T. and Dönitz, J.: TFClass: An expandable hierarchical classification of human transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, D165-D170 (2013).
ChIP-Seq experiment browse pages
New browse page for 161 human DNase hypersensitivity ChIP-Seq experiments imported from ENCODE. Each data set can be downloaded in .bed format.
The TFBS and DNase ChIP-Seq experiment browse pages can be accessed from the tools menu.
113 new transcription factor binding site ChIP-Seq experiments released by the ENCODE phase 3 project between February 2017 and May 2017. The data sets comprise 1,329,758 fragments bound by 98 distinct transcription factors, of which 66 factors were not yet covered by ChIP-Seq data. For 71 of the sets, an existing positional weight matrix for the respective transcription factor was used together with the MATCH tool to predict altogether 816,574 best binding sites inside the fragments. Predicted best binding sites as well as complete fragments are available in FASTA and BED format via the ChIP Experiment Reports, as are lists of genes in a distance range to the fragments as specified by the user.
Reorganization of the in vivo transcription factor bound fragment section on a Locus Report
To improve clarity, only those fragment are listed that overlap with one of the promoter sequences of the entry. As new information fields, the table contains the relative position of the fragment to the transcription start site (TSS) of promoter, as well as the sequence of the predicted best binding site for the transcription factor inside the fragment.
Improved user data management
The "storage" link in the "my data" menu loads an overview page with usage space statistics for each stored user data file or result list. Obsolete files can be deleted directly to stay within the allotted user space.
Quick search for disease and drug entries
The quick search menu includes now options to search for diseases or drugs by external identifiers, such as MeSH ID, Drugbank ID, or Pubchem CID.
Integration of new clinical trial data sources
Integration of new data on clinical trials from clinicaltrials.gov and OpenTrials, covering studies from, among others, European, Japanese and Australian registries. The number of CT-Disease-Drug assignments increases from 227,170 to 297,373, while the CT-Disease assignments are up from 316,785 to 515,576.
HOCOMOCO v10 matrix library integration
134 mononucleotide position weight matrices based on ChIP-Seq experiments have been incorporated from HOCOMOCO v10 (http://hocomoco.autosome.ru/).
Enhanced human SNP content
The new March 2017 dbSNP Build 150 data for human has been integrated and increases the number of SNPs mapped to human promoter sequences more than two-fold from 34,839,288 in the last release to 73,423,232.
Ensembl version update
Genomic information for genes, promoters, and ChIP fragments for the species human, mouse, rat, macaque, and Arabidopsis is now based on Ensembl release 89.
TRANSPATH content
More than 1,000 new phosphorylation reactions have been added, describing substrates and their phosphosites for key kinases such as ERK1, SYK, Plk1, and Aurora-A/B.
Link-out to BRENDA professional - the comprehensive enzyme information system
Locus reports of genes/proteins with enzymatic function now contain links to BRENDA, which can be accessed by users with a valid BRENDA subscription.
BKL 2016.1 Release (Spring Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Addition of gene ontology (GO) and expression data for genes
Literature curated gene ontology (GO) and expression assignments that were previously only available for transcription factors have been extended to all genes in TRANSFAC for which literature information is available. The addition of this data makes it possible for you to select lists of genes from the database based on shared characteristics using the Ontology Search option. For example, you might select all genes that are expressed in ovarian but not prostate tissue and then perform downstream promoter analysis on those genes to identify shared transcriptional regulators. Alternatively, you may upload your own list of genes and then annotate them with GO and expression information values using the Export feature within the Search Results.
Please note that addition of GO and expression data is specific to the online version of TRANSFAC. At this time it is not included in TRANSFAC download.
New Functional Analysis tool in TRANSFAC
With the addition of GO and expression data TRANSFAC users now have access to the Functional Analysis tool for analyzing lists of genes or miRNAs for the presence of significantly over-represented, shared characteristics. The functional analysis tool is accessed by selecting the "Identify shared characteristics" option under the Tools menu. Once the tool has loaded, you can select a previously saved list of genes (human, mouse, rat, yeast and worm species are supported) or miRNAs (human, mouse and rat species are supported) or upload a new list for analysis. When the list is submitted, a Fisher test is performed and the results of the analysis are provided in a detailed report.
Overlay of experimental information on predicted binding site results
Match and related algorithms use similarity to the consensus sequence of a positional weight matrix to identify potential transcription factor binding sites within your DNA sequence. This type of analysis is inherently independent of overall biological context, considering only the nucleotide sequence and how closely it matches the consensus. In our continuing efforts to enable the use of contextual biological data for interpreting and refining predictions we now specifically flag those predicted binding sites which are supported by curated experimental observations. These observations are of two types: (1) experimentally demonstrated transcription factor-gene binding interactions curated from the literature and (2) experimentally demonstrated regulatory effects observed between a transcription factor and a gene. For more information, please see the detailed description in the user manual.
Advanced ChIP and DNase data options for filtering predicted binding site results
We previously introduced the ability to filter the results of Match and related algorithms by ChIP and DNase hypersensitivity intervals in order to identify the subset of predicted sites that fall within regions of DNA that are likely to accessible to the transcriptional machinery. With this release we have extended the filtering option to make it easy to select a specific experiment that you would like to filter your results by. When you click the "filter" link next to the ChIP or DNase checkbox you can now select from a pre-populated drop down list of experiments that contribute intervals that overlap with your results. In this way you can more easily filter your results using DNase hypersensitivity regions identified in hepatocytes versus regions identified in muscle or other cells.
Addition of Macaca mulatta promoters
We have added to the coverage of mammalian promoters within TRANSFAC and now provide direct access to promoter sequences for Macaca mulatta, the rhesus macaque. The promoters were defined by clustering of Ensembl TSSs according to TRANSFAC's promoter selection algorithm. You can now upload a list of Ensembl identifiers or HGNC gene names for M. mulatta genes and directly submit the search results for Match or other sequence analysis.
BKL 2015.3 Release (Fall Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Transcript-level RNA-seq data analysis workflow
TRANSFAC's expanded step-by-step data analysis tool (accessed within the tools menu) now provides an easy-to-use, guided workflow for transcript-level RNA-seq data. It accepts pre-filtered lists of up- or down-regulated Ensembl transcripts, as well as the complete list of Ensembl transcripts analyzed in the experiment. When a complete list is used you will be guided through selection of the subset to be used for the analysis. In both cases, your data set should be preprocessed such that the expression values are in standard fold-change or other format.
For analysis of gene-level RNA-seq data, please use the existing Gene-level microarray and RNA-seq analysis workflow.
More specific contextual filtering of Match results
Filtering options, available when the genomic coordinates of the sequence are known, leverage experimental biological data to provide context for binding site predictions generated as output of TRANSFAC's Match and other predictive algorithms. Regions of conservation (human-mouse only) as well as ChIP fragment and DNAse hypersensitivity intervals are provided so that you can readily identify the subset of predicted sites that fall within stretches of DNA that are likely to be accessible to the transcriptional machinery under the described experimental conditions. With this release it is now possible to apply more specific filtering criteria. Instead of filtering your data by the presence of any ChIP-seq or DNase hypersensitivity regions, you can now select the specific experiments that you would like to filter your results by. For example, you may choose to specifically filter your results using DNase hypersensitivity regions identified in hepatocytes as opposed to regions identified in muscle cells.
Full sequence graphical view
Use the new "Full sequence view" option in the Sequence summary section of Analysis reports to view the entire sequence decorated with predicted binding sites. Apply any contextual filters as desired and even export the complete sequence graphic as a PDF for easy printing and sharing.
BKL 2015.1 Release (Spring Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
TRANSFAC step-by-step data analysis workflow
The new step-by-step data analysis tool (accessed within the tools menu) provides easy-to-use, guided workflows for the analysis of microarray and ChIP-seq data sets.
The microarray analysis workflow accepts pre-filtered lists of up- or down-regulated genes, as well as the complete list of genes analyzed in the experiment. When a complete list is used you will be guided through selection of the subset to be used for the analysis. In both cases, your data set should be preprocessed such that the expression values are in standard fold-change or other format.
The ChIP-seq analysis workflow accepts sequences (FASTA, EMBL, Genbank, or RAW format) or genomic intervals in .bed format which are used to extract the corresponding sequence. Human hg38/GRCh38, mouse mm10/GRCm38 and rat rn5/RSGC 5.0 are supported.
Contextual filtering of Match results
Match and related algorithms use similarity to the consensus sequence of a positional weight matrix to identify potential transcription factor binding sites within your DNA sequence. This type of analysis is inherently independent of overall biological context, considering only the nucleotide sequence and how closely it matches the consensus. With this release it is now possible, when genomic coordinates are known for the sequence, to leverage available experimental biological data to provide contextual filtering. Intervals of conservation (human-mouse only) as well as ChIP fragment and DNAse hypersensitivity intervals are provided so that you can readily identify the subset of predicted sites that fall within regions of DNA that are likely to accessible to the transcriptional machinery under the described experimental conditions.
PGMD (Pharmacogenomic mutation database) variant summaries
PGMD Variant Reports provide information about published sequence level changes that have been associated with a phenotypic effect on drug response. For well-studied variants the number of studies described in the report can be quite extensive, sometimes making it challenging to quickly zero in on the most critical information. With this release a Variant Summary field has been introduced at the top of the Variant Report, providing a short free text summary of the key take away points for a variant. Links to the supporting studies are provided for access to further details.
Please note that not all Variant Reports offer the Variant Summary field at this time, but that increasing numbers of reports will be covered with each biweekly data update.
For further ease of use, the summary field is now followed by an Overview of studies published for the variant. This summary table provides, for each study described within the variant report, an overview of the drug that was the focus of the study, the disease that was being treated as part of the study, the phenotype(s) measured by the study, special notation for phenotypes that are related to FDA recommendations, survival or drug response, whether the variant was studied by itself or as part of a haplotype and the PubMed ID of the reference from which the information was curated. Use the column headers to sort the data in combination with the header search option to easily zero in on critical FDA recommendation and survival phenotypes or other phenotypes of interest. Use the provided study links to jump down to the detailed study description.
BKL 2014.3 Release (Fall Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Introducing the F-match algorithm from ExPlain
Match searches for transcription factor binding sites using compiled positional weight matrices. The new F-match algorithm builds on Match, allowing you to identify sites which are over-represented in a set of analyzed sequences (for example, promoters from differentially expressed genes or ChIP-Seq fragments) in comparison to a background set (for example, promoters from genes whose expression did not change under the same conditions or a set of random sequences).
In addition to providing this new analysis option, the Predict binding sites tool now provides the ability to upload a list of genes for analysis. When this option is selected the genes will be mapped to their corresponding promoter and that promoter sequence will be used for the analysis. This feature is only supported for the following species: human, mouse, rat, A. thaliana, G. max and O. sativa.
Identifying motifs in unaligned sequences
The Create matrices tool now provides the option to identify motifs within unaligned sequences using the DECOD algorithm (Huggins et al, 2011, Bioinformatics 27:2361), and to create a matrix based on the identified motif. Once the matrix has been created, it can be used to analyze sequences for transcription factor binding sites.
BKL 2014.1 Release (Spring Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
TRANSFAC transitions to genomic coordinates for human, mouse and rat entries
This release brings significant content updates and additions due to the transition from TRANSFAC's traditional relative coordinate system for promoters to the standard genomic coordinate system. These updates and additions include:
- Updated promoter sequences - New virtual TSSs have been calculated as reference points for promoter extraction based on the collection of Ensembl transcript start site positions (defined as the first nucleotide of the most 5' exon of an Ensembl model) associated with human, mouse and rat protein- and miRNA-encoding genes. For each virtual TSS calculated, a promoter entry is created and the promoter sequence is extracted as the interval 10,000 nucleotides upstream to 1,000 nucleotides downstream of the defined virtual TSS. A complete description of the virtual TSS calculation process can be viewed here.
- Literature curated binding sites mapped to genomic coordinates - The majority of experimentally determined binding sites curated from the published literature have been mapped to genomic coordinates.
- Integration of ENCODE ChIP-Seq and DNase hypersensitivity data sets - The coverage of ChIP-Seq factor and histone modification experiments has increased through the integration of additional ENCODE data sets. DNase hypersensitivity intervals, previously integrated in the relational database but not displayed online, are now integrated into Promoter and Locus reports as well as into the flat files which are provided by a download subscription.
- Match-based enhancement of ENCODE ChIP-Seq and DNase hypersensitivity data sets - TRANSFAC's Match algorithm for prediction of transcription factor binding sites has been used to identify the portion of the reported fragment that is most likely to have been bound by the transcription factor under investigation in a ChIP-Seq experiment, or to identify the transcription factors that are most capable of binding within a region of accessible DNA as defined by DNase hypersensitivity. The identified binding sites are now integrated into Promoter and Locus reports as well as into the flat files which are provided by a download subscription.
- Updated promoter features - Additional promoter features including repeat elements, CpG islands and SNPs have been updated and mapped to the set of newly defined promoters.
Intevals of cross-species conservation are added to Match analysis
To provide greater biological context to Match analysis results, regions of conservation between species â as defined by the 46 and 60 way phastcons placental elements tracks for human and mouse at UCSC â are now overlaid on Match results when the genomic coordinates of the input sequence is known, either through upload of sequences via genomic coordinates or via analysis of TRANSFAC defined promoter sequences.
Introducing a new algorithm to search for pairs of transcription factor binding sites
Match searches for transcription factor binding sites using
positional weight matrices for single factors. Such an approach can
be critically important for filling in gaps in the published
literature that we know exist, but it can also suffer from overly
optimistic prediction. One way to balance this potential weakness
is to perform a more selective search for pairs of transcription
factors that work together to co-regulate genes.
It is well known from the literature that transcription factors
often act together through closely located DNA binding sites, in
combination with physical factor-factor interactions, to
coordinately regulate gene expression. TRANSFAC uniquely provides
information on hundreds of experimentally documented cases of
coordinate regulation. With this release, we have introduced a new
algorithm that uses models of coordinate regulation to search for
pairs of transcription factor binding sites. When the 'Composite
model â search by pairs of TFs' analysis method is selected in
the Predict TF binding site tool, a set of models prepared from the
literature-documented cases of coordinate regulation is provided.
Alternatively it is possible to create a new, custom model using
any of the matrices provided within the extensive TRANSFAC matrix
library or matrices that have been individually uploaded. The
resulting report shows a summary plus detailed accounting of all
pair-wise binding sites identified.
BKL 2013.4 Release (Winter Data Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
New content
In addition to adding the latest research findings across all content areas of PROTEOME and TRANSFAC, this release introduces more than 2,000 new positional weight matrices (PWMs) to TRANSFAC. These matrices were generated using a new 3DTF approach for determination of PWMs based on 3D modeling methods, which was specifically employed for the set of transcription factors that did not have a previously associated PWM due to an insufficient number or lack of experimentally determined binding sites. The new PWMs are identified by their assignment to the new '3D structure-based energy calculations' category. For more information about the 3DTF method, please see the recent Nucleic Acids Research publication by Gabdoulline et al.
BKL 2013.3 Release (Fall Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
PGMD™ launch
The PharmacoGenomic Mutation Database (PGMD™) is a resource for identifying all published genetic variants that have been shown to affect drug response in patients. We have mined the scientific literature for every in vivo patient study that has yielded a significant correlation between genotype and drug response, and offer multiple delivery models for accessing this data, including an intuitive exploratory interface and a data download for integration with in-house analysis pipelines.
Use PGMD™ with Genome Trax™ or ANNOVAR™ to annotate drug response variants within an individual's genome.
Integration of ExPlain functionality into PROTEOME + TRANSFAC - Phase II
During the course of the coming year we will be integrating the functionality of the ExPlain analysis platform into the PROTEOME + TRANSFAC offering - a project that we are undertaking in order to provide a stronger foundation from which to provide (1) immediate access to quarterly data updates for use in analyses and to (2) develop more advanced analysis capabilities. With this release we have completed the second phase of the integration. This phase introduces the following features:
- Analysis scheduling system - The BKL analysis scheduling
system allows select analysis tools to run in the background,
allowing you to move on to other tasks while the analysis continues
to run. Whenever you initiate an analysis for a tool that uses the
scheduling system you will be automatically directed to the new
'taskbar' dashboard which lists each analysis that has been
submitted along with information about its status. For short
analyses, leave the taskbar window open and the results of the
analysis will automatically load upon completion. For longer
analyses, navigate to other tasks as desired then return to the
taskbar and click the link to manually open the results once the
alert icon appears next to the taskbar link.
Analysis results will be automatically deleted after 1 week or once you exceed a maximum of 50 results, whichever comes first. To save a copy of the results permanently, choose the 'Save this result' option within the corresponding analysis report.
taskbar alert
- New version support - In an effort to provide support for data replication for publication purposes, we have introduced support for older versions of matrix libraries for use with Match and older versions of interaction libraries for use in the Network Analysis tool. In both cases the current interaction library will always be selected by default, but you may choose to use an older library version as desired. With this release we are providing support for versions 2013.3 (current) and 2013.2. With subsequent releases we will continue to add support for additional versions, up to a maximum of four versions spanning one calendar year.
- New Match graphical visualization - Graphical
visualization of Match results has been enhanced to provide easier
visualization of, and access to supporting details for, predicted
transcription factor binding sites.
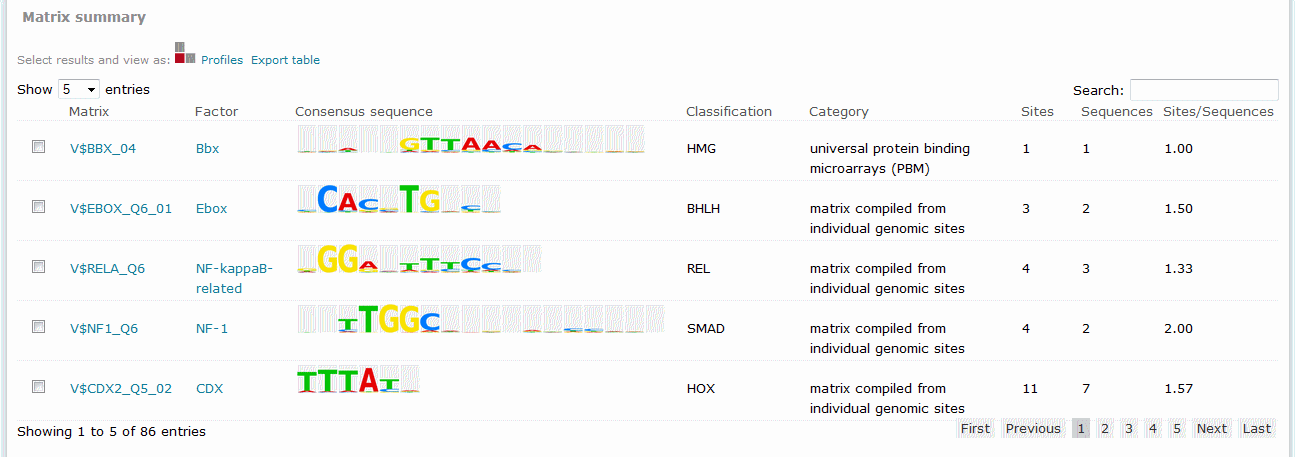
Match predicted binding site results
- New sequence upload for Match analysis using genomic coordinates in .bed format - We now provide the option to upload DNA sequences for Match predicted transcription factor binding site analysis via .bed coordinates. Simply copy and paste or select a file for upload and the corresponding sequence will automatically be extracted from a local copy of the genome and saved in the Sequences folder of the my data tree. Upload of sequences via .bed coordinates is only supported for human (hg19/GRCh37), mouse (mm10/GRCm38) and rat (rn5/RGSC 5.0) genomes and requires strict adherence to .bed format standards.
- New compartment localization view in Pathfinder - The
Pathfinder visualization tool now offers the ability to view
networks and pathways arranged by the cellular location of each
component.
Pathfinder compartment layout
In addition to features related to the integration the following noteworthy content additions have been made:
- Updated vertebrate non-redundant profile (VNR) - Using the previously introduced matrix classification system, we have updated the VNR profile to allow for maximum coverage in concert with reduced redundancy in predicted transcription factor binding site searches. The linked Matrix Report for each representative matrices selected for inclusion in the VNR details the complete list of matrices that are represented by the matrix.
BKL 2013.2 Release (Summer Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Integration of ExPlain functionality into PROTEOME + TRANSFAC - Phase I
During the course of the coming year we will be integrating the functionality of the ExPlain analysis platform into the PROTEOME + TRANSFAC offering - a project that we are undertaking in order to provide a stronger foundation from which to provide (1) immediate access to quarterly data updates for use in analyses and to (2) develop more advanced analysis capabilities. With this release we have completed the first phase of the integration. This phase introduces the following features:
- Centralized data management system - The new 'my data' menu located in the header next to the 'search' and 'tools' menus provides a centralized location for storing all search results, analysis results generated using the tools, as well as all user-uploaded data such as lists of genes/identifiers, FASTA sequences for Match analysis, etc.
- New functional analysis tool - Based on the Functional classification and Canonical pathways mapping tools in ExPlain, and the set analysis feature of PROTEOME ontology search, we have introduced a new tool for analyzing lists of genes or miRNAs for the presence of significantly over-represented, shared characteristics. The functional analysis tool is accessed by selecting the 'Identify shared characteristics' option under the Tools menu. Once the tool has loaded, you can select a previously saved list of genes (human, mouse, rat, yeast and worm species are supported) or miRNAs (human, mouse and rat species are supported) or upload a new list for analysis. When the list is submitted, a Fisher test is performed and the results of the analysis are provided in a detailed report. For subscribers of the PROTEOME API version, the Fisher test analysis can be independently accessed by API. Please note that access to the functional analysis tool requires a subscription to ExPlain or PROTEOME.
- New network analysis tool - Based on the Network clusters tool in ExPlain we have introduced a new tool for analyzing lists of genes for the presence of shared networks. The network analysis tool is accessed by selecting the 'Identify shared networks' option under the Tools menu. Once the tool has loaded, you can select a previously saved list of genes (human, mouse and rat species are supported) or upload a new list for analysis. When the list is submitted, the network cluster analysis is performed and the results of the analysis are provided in a detailed report. Networks identified by the analysis can be directly viewed in the BKL Pathfinder visualization tool where they can be further edited, extended and exported for publication. Please note that access to the network analysis tool requires subscription to ExPlain or PROTEOME.
As a precursor to planned enhancements transcription factor binding site enhancements in phase II of the ExPlain integration we have adapted the format of the Match output.
In addition to features related to the integration the following noteworthy content additions have been made:
- Updated transcription factor classification - Using the TFClass classification of human transcription factors as a basis, we have (1) updated the browsable classification view for mammalian transcription factors and (2) separated plant and fungal transcription factors into their own independent classification trees.
- New HITS-Clip high-throughput analysis of miRNA - Curation of the high-throughput Argonaute HITS-CLIP generated miRNA-mRNA interaction map published in Nature 460:479-86 has resulted in the addition of more than 10,000 miRNA target assignments, all attributed to the new HITS-CLIP method.
BKL 2013.1 Release (Spring Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
New Pathfinder network and pathway visualization features
In addition to the regular quarterly expansion of content covering protein-protein interactions, directed signaling events (including enzymatic events such as phosphorylation, dephosphorylation, acetylation and more) and transcription factor-mediated gene-regulation networks, we have continued to expand the functionality of the Pathfinder tool for visualization of these networks as well as the canonical pathways that they form the basis of.
The enhancements include:
- Introduction of a persistent node information panel that you control the placement of
- Summary description for each gene/protein/miRNA on the canvas upon selection of the node
- One click access to the full list of interacting partners for a selected node
- Ability to search and filter the list of interacting partners by gene/protein/miRNA name, interaction type, effect and more
- A new layout option that takes the literature-curated cellular location for the node into consideration when drawing the network
Miscellaneous improvements for ease of use
A number of helpful features have been added to make it easier to find the information that you are looking for and to carry out your desired analyses.
These features include:
- Autocomplete suggestions for Genes and proteins, miRNAs, Diseases, Drugs, Pathways and Transcription factors 'Name' searches which are accessible under the 'Click here for more search options' link
- Improved filtering capability in the Match profile generation tool (TRANSFAC only)
BKL 2012.4 Release (Winter Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Expanded and new miRNA content
miRNAs are small RNAs that post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression through sequence-specific binding that typically promotes mRNA degredation or prevents mRNA translation. In recent years aberrant miRNA expression has been linked to numerous diseases, fueling research into these important regulators and their targets.
With this release we have integrated structural data from miRBase (host gene assignments, miR clusters, miR families and TargetScan seed families) with the high quality literature-curated content that BIOBASE is known for. The curated content for miRNAs includes:
- Summary title lines describing the most important physical and functional features
- Functional assignments (GO molecular function, biological process, cellular component)
- Organ, tissue, cell and tumor expression patterns
- Disease associations for miRNAs
- Disease associations for miRNA targets (PROTEOME™ only)
- Experimentally validated miRNA-target interactions (TRANSFAC® only)
The new miRNA Report presents the combined public domain and proprietary curated information in an organized format for easy viewing. For users who subscribe to both TRANSFAC® and PROTEOME™, uniquely integrated information, such as the disease associations which are shared between an miRNA and its experimentally determined targets, is highlighted.
Specialized search functions allow for easy identification of shared targets among a list of uploaded miRNAs (Agilent, Exiqon, Taqman and miRBase identifiers are supported). Selected miRNA-target interaction networks are easily viewed and expanded in the Pathfinder visualization tool.For more information, see our miRNA feature overview.
New matrix classification tool
Do you have a custom positional weight matrix that you've identified through binding experiments? Now you can quickly and easily compare your matrix against the TRANSFAC® matrix library to identify whether a related matrix exists or whether your matrix represents a newly identified motif. Simply create your matrix in TRANSFAC® using a set of aligned binding sites, or upload a matrix file in TRANSFAC®'s matrix.dat format, and launch the new matrix comparison tool found under the Tools -> Create and compare matrices option. Using the developed m2match algorithm (Stegmaier et al, article submitted), the tool compares your matrix to the TRANSFAC® matrix library to identify motifs describing similar patterns.
For more information, see our example matrix comparison.
BKL 2012.3 Release (Fall Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
The new look of TRANSFAC and PROTEOME is officially here
The TRANSFAC and PROTEOME interface has been updated to provide a more intuitive and user-friendly experience. Thanks to everyone who took the time to provide feedback on the preview version. If you haven't had a chance to take our survey and tell us about your experiences we'd still love to hear from you. Find out more about the transition and provide your feedback here.
The new BKL Pathfinder visualization tool is launched
With the official release of the new interface we are launching a new BKL Pathfinder visualization tool. You'll still find all of the previous features such as disease and drug highlighting, in addition to a new graphic presentation and support for multiple layout options.
Take a peek at the new look:
To try it out, open the Tools menu and click the 'View pathways and build networks' link.
Use Match to predict transcription factor binding sites for TRANSFAC promoters
With this release you can now launch a Match analysis for predicting transcription factor binding sites directly from search results and locus reports. Simply select the gene or genes of interest, click the new Match icon, set the requested parameters in the pop-up window that opens, and start your analysis.
BKL 2012.2 Release (Summer Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
A preview of the new look of TRANSFAC and PROTEOME is here
The TRANSFAC and PROTEOME interface has been updated to provide a more intuitive and user-friendly experience. Find out more about the transition and provide your feedback here. The new interface will be officially launched in fall 2012.
BKL 2012.1 Release (Spring Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Expanded positional weight matrix content
TRANSFAC has long been the gold standard for positional weight matrices, and now with this release we've gone beyond the standard quarterly update of new material to include:
- New positional weight matrices generated using a unique 3D-structure based computational method (see Alamanova et al, BMC Bioinformatics 2010 11:225)
- A new method classification scheme for matrices
- New linking between related factor-specific and family matrices
- New links to related matrices from other resources
- Redesigned matrix reports that make it easier to see the experimental evidence from the literature for the binding sites that underly many of the Transfac matrices
ChIP-ChIP and ChIP-seq experiment reports
With this release, ChIP-ChIP and ChIP-seq data sets within ExPlain have been elevated to the level of having their own report. Each report provides a summary of the experiment, combined with direct links to pre-processed data that is made available for easy export or import into supplementary tools for further analysis. For example, import the list of associated genes into the Ontology Search tool in order to identify over-represented functions associated with the genes potentially regulated by the transcription factor. Or import the list of associated genes, or the FASTA sequences for the fragments, into the ExPlain analysis platform in order to identify potential co-regulatory factors.
A more powerful and easy to use visualization tool
With this release we've upgraded the underlying Pathfinder system in order to deliver fast, responsive loading of canonical pathways and user directed networks. We've also added many new features including:
- A new preview pane for large data sets which provides the user with an overview of all reactions that will be added to the canvas, coupled with tools for filtering of the data set by reaction type or molecule type - so you have more control over the size of the network
- Easier access to the experimental evidence supporting displayed association as well as the reference from which the observation was derived
BKL 2011.4 Release (Winter Data Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
PROTEOME API Web service
In June of 2011 we introduced a collection of perl programs that make it easier for customers who subscribe to the installed PROTEOME relational database to extract data sets of interest. These data sets may then be incorporated into customized internal pipelines and bioinformatics platforms, or adapted versions of the programs may be called directly within customized tools. Now, in our latest effort to provide programmatic access to PROTEOME data, we've introduced an API that allows subscribers to:
- Directly extract desired fields of information from locus, disease, drug, and pathway reports in XML format
- Analyze a set of genes for over-represented biological process, molecular function, and disease term assignments using either a simple Fisher test or LR Path (logistic regression) algorithm
BKL 2011.3 Release (Fall Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Information about Toxicity Bioassays Added to Drug Reports
With this release, we've added information to our PROTEOMETM Drug Reports about toxicity bioassays that have been investigated for the drug of the page as reported by the FDA published in the following reference:
Matthews, E.J., Kruhlak, N.L., Cimino, M.C., Benz, R.D., and Contrera, J.F. An Analysis of Genetic Toxicity, Reproductive and Developmental Toxicity, and Carcinogenicity Data: I. Identification of Carcinogens Using Surrogate Endpoints. Regulatory and Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2006.
This data is also included as a Drug hierarchy in the Ontology Search tool in order to facilitate searches for drugs sharing similar toxicity profiles. Assays are grouped into three categories: carcinogenicity, genetic toxicity, and reproductive and developmental toxicity.
Quick and Advanced/TRANSFAC Module Search Improvements
With this release the Quick Search is even quicker - check it out and benefit from its quick lookup power.
Plus the Advanced and TRANSFAC Module searches are now smarter and more user friendly. Select the entity that you wish to search for and your preference will be remembered for your next search.
Optional XML Output for Command Line BioKnowledge Transfer Tool
For subscribers to the installed PROTEOMETM relational database, the included command line BioKnowledge Transfer tool now supports validated XML output for easier parsing. For more information about the BioKnowledge Transfer tool, see the description under the "New Sequence Annotation Tool is Launched" section of the 2011.1 release notes.
Relational Database Query Options
We understand that computational analyses are only as reliable as the data upon which they're based and that a single online solution does not fit all needs - which is why we provide the option to license the installed, relational content for bioinformatics and computational biologist groups.
With the data release in June we introduced a collection of custom perl programs that make it easier for customers who subscribe to the installed relational database to extract data sets of interest which can be incorporated into customized internal pipelines and tools. These programs cover topics such as identifying drug targets and their associated pathways, identifying orthologs of a given human, mouse or rat gene, extracting fold-change values for yeast genes following exposure to agricultural fungicides, and much more.
For installed users who haven't yet taken advantage of these queries, contact us at support@genexplain.com for more information regarding how to gain access.
BKL 2011.1 Release (Spring Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
New Sequence Annotation Tool is Launched
The BioKnowledge Transfer (BKT) tool, part of our PROTEOMETM product, is a custom sequence annotation tool for functional annotation of next generation sequences from uncharacterized genomes. This tool enables researchers to input protein sequences and extract functional information on the proteins based on those sequences. The functional predictions are drawn from domain and GO assignments for homologous proteins derived from over 15 years of manual curation on mammalian, yeast, worm, and plant species.
The BKT tool fits into your sequence analysis workflow:
Match Interface
Reports include alignments and GO predictions with links to additional supporting details.
Disease Biomarker, Drug Targets, and Pathway Data is now Included in Genome Trax
In addition to new feature types, this release also provides:
- Expanded data input options including the ability to input variants by tab- or space-delimited coordinates, UCSC notation, or by direct file download from accessible HTTP or FTP URLs.
- The ability to isolate the subset of features that are simultaneously disrupted by a single variation.
Pathfinder Enhancements
The Pathfinder visualization tool now provides the ability to export a PNG image of the canvas - so that you can now easily capture the customized network you've created for use in reports and presentations. Alternatively, you can now also export the data for your network in GML format, for use in applications such as Cytoscape.
Introducing a New Look for the Match Interface
You'll find all of the features that you know and rely upon for your transcription factor binding site analyses, just with a more modern presentation coupled with greater ability to manage your data, including easy access to:
- your uploaded sequences
- your created Matrices and Profiles
- your saved Match results
BKL 2010.3 Release (Fall Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
New Genome Trax™ Tool is Launched
Genome Trax™ is a brand new product from BIOBASE designed for use in Next Generation Sequencing analysis. It is composed of genome feature tracks that can be mapped to your next generation sequences and help you decipher the significance of your sequence variations. Tracks include inherited disease mutations from HGMD, transcription factor binding sites from TRANSFAC, SNPs, promoter features, post-translational modifications, and more! You can use Genome Trax with BIOBASE's own online mining tool, or with well-known genome browsers including UCSC and CLC Genomics Workbench.
New Clinical Trials Data
BIOBASE has integrated clinical trials data from ClinicalTrials.gov, mapping Intervention entries of type "Drug" to BKL drug entities and Condition entries to BKL disease entries which results in a unique controlled vocabulary data structure that links drugs and diseases to each other as well as proteins, pathways, and other biological entities. View the new data within the new Clinical Trials section of Disease Reports and Drug Reports, or make use of it within the expanded Ontology Search tool.
Expanded Ontology Search Tool
The structured content of the BIOBASE Knowledge Library and its unique BKL Ontology Search platform has long offered a solution for quickly, easily and reliably answering complex biological questions. With this release, the Ontology Search tool has been expanded to allow users to answers questions from the perspective of a disease or a drug, in addition to the traditional perspective of a protein. Easily answer questions such as:
- Which diseases are associated with an altered immune response? Which of those are the subject of a clinical trial in phase 3 or later?
- Which diseases are known to co-occur with hypertension?
- Which drugs are under investigation for treatment of Diabetes? What pathways are those drugs associated with?
BKL 2010.2 Release (Summer Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Yeast and Worm Report Improvements
Yeast and worm researchers can now find the detailed information they're looking for even more easily than before with new report navigation features and expanded external links including integrated links to:
- Saccharomyces Cerevisiae Morphological Database, providing images of mutant yeast cells
- GPMDB, providing peptides characterized by mass spectroemtry (yeast and worm)
- PhosphoPep Database, providing sites of phosphorylation (yeast and worm)
- Phylome DB, providing phylogenetic trees for yeast genes
- Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (CGC), providing information regarding available C. elegans strains
- gfpworm.org, providing expression patterns for C. elegans promoter::GFP fusions
- WormAtlas Handbook, providing information regarding behavioral and structural anatomy of C. elegans
New Histone and DNA Modifcation (Methylation, Acetylation) Data
TRANSFAC flatfile now customers have access to this unique data set of over 3,000,000 promoter fragments containing histone and DNA modifications (methylations and acetylations), facilitating histone/DNA modification genomic distribution analyses.
BKL 2010.1 Release (Spring Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Product Consolidation
The BIOBASE Knowledge Library has been consolidated into three offerings: BKL PROTEOME, BKL TRANSFAC, and the complete BKL (PROTEOME + TRANSFAC). The effect of this change will be minimal, generally resulting in increased content available with your subscription.
Note that users are now able to set Quick Search preferences for preferred species, to simplify navigation through the additional content.
New Look and Faster Performance
Google-like Quick Search behavior and a new, simplified design for searches and reports makes it even easier and faster to find what you're looking for.
Export Controlled Vocabulary Assignments
The new Export option for genes and proteins allows you to export controlled vocabulary assignments in a tabulated format. Topics available for export include disease, drug, gene ontology, expression and more.
Expanded HGMD Content
View an overview of mutation content offered in HGMD® (Human Gene Mutation Database). Note that access to the full content requires subscription to HGMD
BKL 2009.3 Release (Fall Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
New TRANSFAC® Chip-Seq Data
New to Transfac® Professional, over 500,000 ChIP-Seq regions from the human and mouse genomes, derived from next generation sequencing technology, as well as 57,000 RNA Polymerase II binding regions from the human genome are available to users.
TRANSFAC® Complex Reports now contain Gene Regulation Data and Links to Chip-chip Data
Complex reports now contain gene regulation information, including sites bound by the complex and links to the Browse by TF feature to access Chip-chip sequences bound by the complex.
New Drug Information
BKL Locus Reports, Retriever Tool, and Pathfinder allow you to view protein-drug associations from Drugbank. New Drug Reports provide information on proteins which are therapeutic targets of the drugs or which metabolize the drug, as well as pathways affected by the drug and relevant drug information.
Locus Reports
A new "Drug Interactions" section lists drugs which either affect the protein of interest or are metabolized by the protein.
Drug Report
New Drug Reports contain detailed information on therapeutic protein target, associated diseases, proteins that metabolize the drug, pathways involved in drug activity or metabolism, and clinical information including synonyms, half-life, adverse effects, and biotransformation.
Retriever
The BKL Retriever contains a new "Pharmaceuticals" hierarchy, derived from drug hierarchies shared by MeSH and PubChem. Users may use this hierarchy to identify proteins associated with drug classes.
Pathfinder
The BKL Pathfinder contains a new "Highlight Drug" feature, which allows users to overlay information on drugs which interact with proteins in the observed network.
Disease Biomarker Indications
In the "Biomarker Associations" section of HumanPSD Locus Reports, a new section called "Indications" describes what the biomarker/disease association may indicate about the utility of the biomarker, including its use for determining disease mechanism, prognostic value, or potential as a therapeutic target.
Reorganization of Locus Reports
Locus Reports have been reorganized to simplify the user experience, with better grouping of disease, gene, and protein specific data.
Extract Promoter Sequences by Coordinates
When conducting an advanced promoter search, users may extract promoter sequence(s) by coordinates, ranging from -10,000 to +1,000. Users may choose several export formats, including FASTA, TransPro, EMBL, Genbank, or DDBJ.
Export Site and Matrix Lists as Profiles for Match and Patch Command Line
Matrix and Site search results can now be used for Match and Patch analysis using command line. Search results can be imported directly into the Match Profiler, and Site search results can also be directly exported into Patch from the search results.
Selecting Reactions by Type in Pathfinder
When accessing the node menu, users can now choose different reaction types to display, including gene regulation, pathway step, molecular evidence, and semantic.
Multi-sequence BLAST
Up to five sequences in FASTA format can now be entered into the BLAST search tool. Results are separated by each sequence that was entered.
Webservices for PDB Protein Structures, BAR Arabidopsis eFP Viewer, and Reference Abstracts
PDB 3-D protein structures are displayed in the Protein Section of Locus Reports. In BKL-Plant, previous links to the BAR Arabidopsis and Cell eFP Viewer are replaced with a webservice display, and references throughout the product allow users to read full abstracts, providing more in depth reference information.
Addition of full Sorghum bicolor proteome
The full proteome of Sorghum bicolor, with PFAM domains, GO assignments, BLAST data, and Model Organism homolog data, are available in BKL-Plant.
BKL 2009.2 Release (Summer Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Transcription Factor Classification Hierarchy
The expandable view of the Transcription Factor Classification hierarchy that was available in the traditional TRANSFAC interface has now been reintroduced in the new BKL interface, located under the Advanced Search menu. Click the hyperlinks provided to directly access the relevant Family Report or Locus Report.
Browse by TF
A new overview of transcription factors with associated ChIP-chip fragments is provided via a new "Browse by TF" link in the Advanced Search menu. Click the binding factor hyperlinks provided to directly access the Locus Report for the relevant transcription factor, or click the provided Export buttons to export the set of associated fragments in FASTA format or to export a tab-delimited list of genes that are associated with the fragments.
New Plant Species Information in BKL-Plant and TransPro
The soybean (Glycine max) genome has been added to BKL-Plant and corresponding the corresponding promoters are also available in TransPro. The sequences are derived from the DOE Joint Genome Institute Soybean Sequencing Project. Functional assignments are provided via BIOBASE's proprietary BioKnowledge Transfer process.
BKL 2009.1 Release (Spring Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Search
Quick Search identifier search has been expanded to include BKL identifiers for all data types (i.e. matrix, reaction, etc).
A new Quick Search entry point allows you to search directly for disease biomarkers. The Disease Quick Search has been renamed Disease Biomarkers and now offers the ability to query directly by gene/protein name.
The Gene set analysis button provided in the Quick Search view provides direct access to the upload feature of the BKL Retriever. This tool can be used to upload a set of genes, statistically analyze them for over-representation by disease, expression, canonical pathways, etc, and to create a customized report summarizing the findings.
Tools
BKL Pathfinder
The BKL Pathfinder now includes synthetic lethal relationships for yeast genes as well as indirect regulator information for yeast and worm genes/proteins.
Reports
The Disease section of human Locus Reports (renamed Biomarker Associations) has been reorganized to show at-a-glance whether the association is causal, correlative, preventative, or negative. Direct access to a customized summary of each gene/protein-disease relationship is provided via [details] links. The customized summary is provided in a tabulated format that promotes easy sorting and comparison of the data.
Disease Reports have similarly been reorganized to list the associated gene/protein biomarkers and to show at-a-glance whether the association is causal, correlative, preventative, or negative. Direct access to a customized summary of each gene/protein-disease relationship is provided via [details] links. The customized summary is provided in a tabulated format that promotes easy sorting and comparison of the data. A customized search tool has been added to the Disease Report that allows you to return the list of associated gene/protein biomarkers directly (filtering as desired by such criteria as those that are specifically expressed in serum, etc) for export in tab-delimited format or for direct input into the BKL Pathfinder tool.
Expression information for mammalian genes is provided in a new, tabulated format that makes it easy to see at-a-glance whether the mRNA, the protein, or both have been experimentally detected in each tissue/organ, cell, or tumor type assigned.
TRANSFAC binding sites are now directly highlighted on promoter sequences.
Locus Reports can now be directly loaded from external applications by providing the species and gene name within a template URL. This is in addition to the existing ability to load Locus Reports by providing EntrezGene and UniProt identifiers and to load Small Molecule Reports by providing PubChem identifiers. For more information on how to construct the various URL templates, and for the species supported, please see the BKL Reports section of the Help documentation.
BKL 2008.2 Release (Winter Software Update)
Note: some of these updates are product specific. Such features may only be available if you have the corresponding database subscriptions.
Search
Quick Search now has a built in "browse" function. When submitting a search without any search criteria, 1000 sample Locus Reports are listed. For Advanced Search, the reports matching the search are listed, for example, Promoter Search will list Promoters. Search Results are capped at 1000 records.
Drop-down menus in the Quick Search now enable you to limit your name searches to certain species or identifier searches to certain kinds of identifiers.
A new TF Classification Search allows users to browse the transcription factor family hierarchy to find factors of interest.
Some small bugs, for example when using special characters in search strings, were fixed.
Tools
BKL Pathfinder
The BKL Pathfinder now automatically loads the neighborhood of connected genes and proteins when a gene/protein is imported. In the case of many interacting partners of a gene/protein this can lead to an alert message. Please see the BKL Pathfinder documentation for suggestions on how to work around this alert. Layout of edges and rendering speed has been improved.
It is now possible to save and reload your own networks.
Several bugs relating to visualization and highlighting of pathways and chains were fixed.
MATCH
Due to popular demand, MATCH is once again provided directly from the tools menu for subscribers of TRANSFAC. More sophisticated options for sequence analysis are available through ExPlain, via the ExPlain link.
Reports
Due to popular request, the Related Proteins section of the Locus Report once again provides a summary of related proteins across all species regardless of subscription. To reduce data download size for installed customers, BLAST results stored in the database are limited to the top 5 hits for each species. The detailed summaries of BLAST results provided in the Related Proteins section of the Locus Report are now calculated on-the-fly rather than calculated and distributed. For installed customers, a working BLAST must be available.
For online customers, we now provide links to reagent providers to make it easier to order research tools like antibodies or clones. These are located in the Research Tools section near the top of the Locus Report.
Phenotype information for closely related model organism homologs (i.e. yeast, C. elegans) is now provided on Locus Reports.
Arabidopsis Locus Reports now contain hyperlinks to BAR Arabidopsis eFP Browser and Cell eFP Browser which display virtual representations of microarray expression and subcellular localization data.
Hand-drawn maps for important signaling and metabolic pathways are now accessible by direct links in the reports of the proteins, genes and small molecules.
The layout, graphics, naming and consistency of presentation in the reports have been improved in many small ways.
Administration and Configuration
The Statistics, Errors, and Process list menu options in the Administrator menu are no longer available in installed builds as these were originally provided for internal testing and are no longer required.
Installation
For installed customers, a master installation script is now provided that seamlessly executes what were previously independent scripts. The master script assumes the presence of a valid setup.rc file, but incorporates basic checking of the settings provided in this file to help ensure that the appropriate settings are in place. Please see the provided installation manual for more information about the master installation script and the setup.rc file.