BioKnowledge Transfer Tool
Introduction
The BioKnowledge Transfer tool is accessible from the search pull-down menu of the main BKL page, shown in Figure 1, by clicking on the Predict protein attributes link . The tool provides an on-line interface where subscribers to the on-line version of PROTEOME can submit a protein sequence for customized functional annotation. The tool has been developed as an automated workflow which employs the same steps as BIOBASE's proprietary manual BioKnoweldge Transfer (BKT) curation process which is based on Pfam domain analysis (using HMMer 3.0) and BLAST analysis that leverages the vast wealth of functional annotation provided for more than 220,000 characterized sequences across more than 20 species within the PROTEOME offering. For each protein submitted, the tool provides an automatically generated title line (describing similarity to the best characterized BLAST hit, function of the best BLAST hit, and membership in conserved families or the presence of conserved domains or motifs), the best characterized BLAST hit, the domain structure, and applicable GO terms.
BioKnowledge Transfer Tool Interface
The BioKnowledge Transfer Tool interface provides users with the ability to copy and paste or upload a set of FASTA protein sequences.
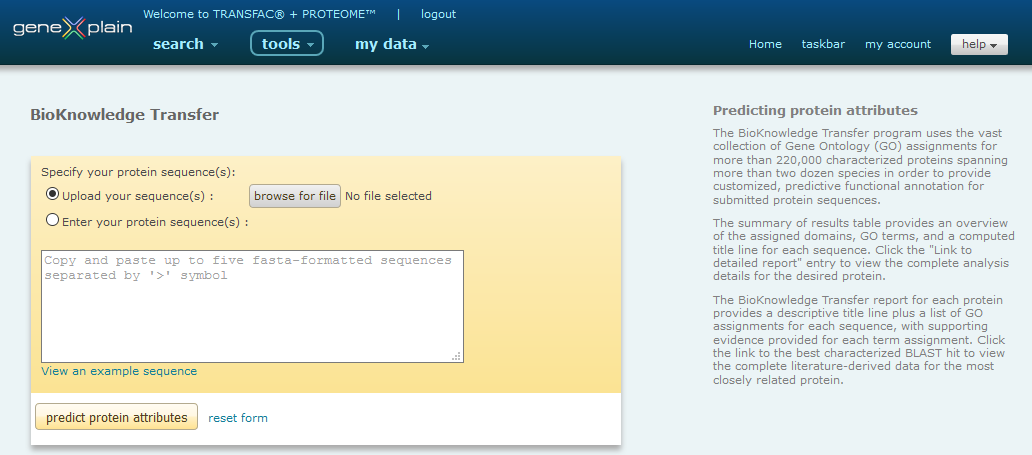
BioKnowledge Transfer Tool interface
Only FASTA formatted sequences are accepted. Multiple sequences, up to a limit of 5, can be submitted if separated by a '>' symbol.
Example FASTA sequence:
>EG:87B1.3 [Drosophila
melanogaster]
MRFQQLLHVRRLASAGATTLMRRPITTTTITTTSRTALAATYPAFATTVRTMAGSGAPIPELTEITDNVQ
RGNYATLTDKDVAHFEQLLGKNFVLTEDLEGYNICFLKRIRGNSKLVLKPGSTAEVAAILKYCNERRLAV
VPQGGNTGLVGGSVPICDEIVLSLARLNKVLSVDEVTGIAVVEAGCILENFDQRAREVGLTVPLDLGAKA
SCHIGGNVSTNAGGVRVVRYGNLHGSVLGVEAVLATGQVLDLMSNFKKDNTGYHMKHLFIGSEGTLGVVT
KLSMLCPHSSRAVNVAFIGLNSFDDVLKTFVSAKRNLGEILSSCELIDERALNTALEQFKFLNSPISGFP
FYMLIETSGSNGDHDEEKINQFIGDGMERGEIQDGTVTGDPGKVQEIWKIREMVPLGLIEKSFCFKYDIS
LPLRDFYNIVDVMRERCGPLATVVCGYGHLGDSNLHLNVSCEEFNDEIYKRVEPFVYEYTSKLKGSISAE
HGIGFLKKDYLHYSKDPVAIGYMREMKKLLDPNSILNPYKVLN
Each sequence can be preceded by a user-defined name (i.e. EG:87B1.3 Drosophila in the above example). If no name is provided, the sequence will automatically be provided with an internal system identifier when processed.
BioKnowledge Transfer Tool Output
The BioKnowledge Transfer Tool output consists of a table containing a summary line for each of the proteins submitted.
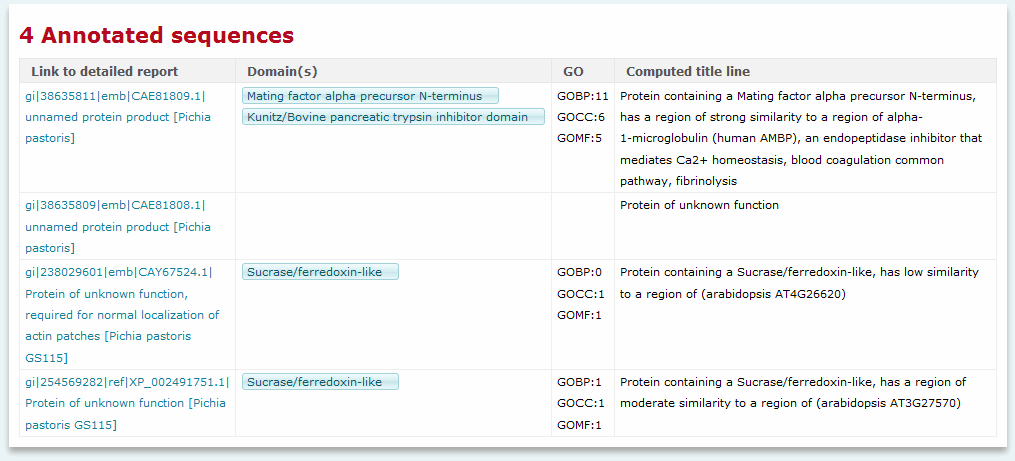
BioKnowledge Transfer Tool output - summary view
For each protein the following information is provided at-a-glance:
- Sequence - the user-defined name for the submitted
sequence, or the automatically assigned internal system identifier
for cases where no user-defined name is provided
- Domain(s) - the list of unique Pfam domains
identified
- GO - a check mark indicates that at least one GO term
has been assigned to the sequence
- Summary - the predictive title line describing
similarity to the best characterized BLAST hit, function of the
best BLAST hit, and membership in conserved families or the
presence of conserved domains or motifs
Clicking the link formed by the sequence name opens a detailed report.
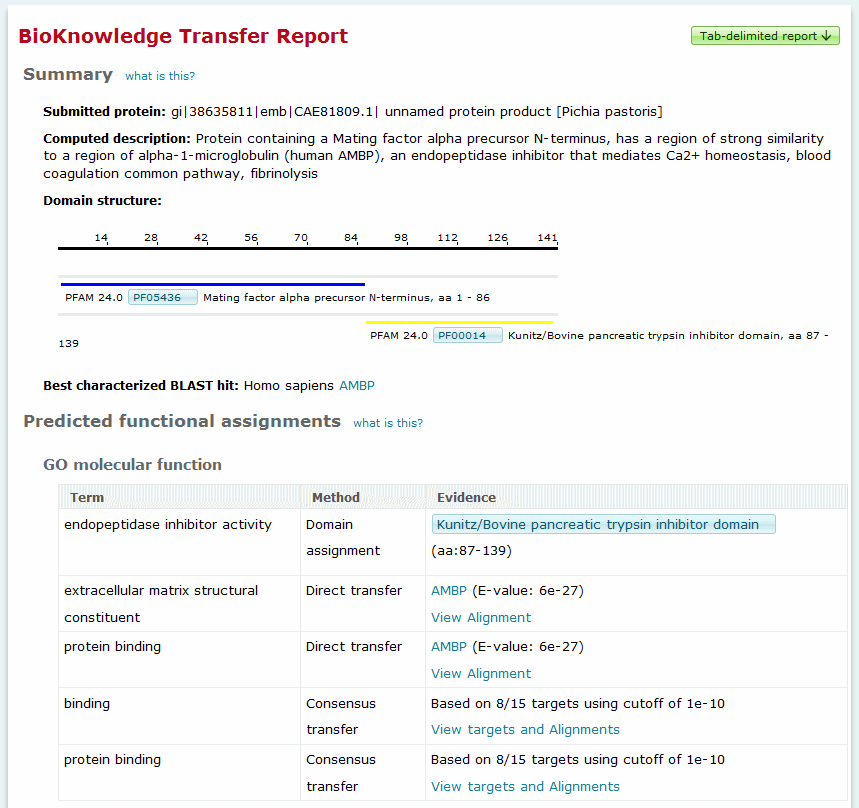
BioKnowledge Transfer Tool output - detailed sequence report view
The detailed report provides links back to the summary report plus an option to export the report's contents. The report provides the following information for the sequence:
- Submitted protein - the user-defined name for the
submitted sequence
- Computed description - the predictive title line
describing similarity to the best characterized BLAST hit, function
of the best BLAST hit, and membership in conserved families or the
presence of conserved domains or motifs
- Best characterized BLAST hit - identifies the best
scoring BLAST target that is considered to be "characterized" and
provides a link to the full Locus
Report for the target. For more information about which
proteins are considered as "characterized" and how this affects
ranking of BLAST targets, please see the detailed description of
the BLAST analysis process.
- Domain structure - provides a graphical display of the
Pfam domains identified within the sequence. For more information
about how domain assignments are made, please see the detailed
description of the Pfam analysis
process.
- Predicted functional assignments - provides predicted GO
terms broken down by molecular function, biological process, and
cellular component topics. GO terms are assigned by one of three
methods which are indicated in the methods column:
- Domain assignment - based on Pfam analysis. Provides a link to
the Pfam report for the domain.
- Direct transfer - based on GO terms curated to the best
characterized BLAST target. Provides a link to the BLAST alignment
and Locus Report for the best
characterized target.
- Consensus transfer - based on the collection of GO terms
curated to the full set of BLAST targets. The ratio of targets
containing the term assignment to the total is provided with a link
to the BLAST alignments of the top 5 hits.
- Domain assignment - based on Pfam analysis. Provides a link to
the Pfam report for the domain.